...

[Math] 확률의 법칙들
Multiplication Law (곱셈법칙) : intersection 확률이 0이 아닌 2개의 event $A$, $B$에 대해, $$ p(A,B)=p(A\cap B)=p(A)p(B|A)=p(B)p(A|B), (\text{if } p(A)>0,p(B)>0) $$ $p(A,B)$를 흔히 joint probability(결합확률, 연접확률)이라고 부름. Joint probability vs. Conditional probability 술(A)을 마시고 사고(B)가 일어날 확률 ← joint probability 술(A)를 마셨을 때 사고(B)가 일어날 확률 ← conditional probability Addition Law (덧셈법칙) : union 2개의 event $A,B$에 대해 합사건의 확률 (..

[Math] Conditional Probability and Joint Probability
Conditional Probability (조건부 확률)Event $F$가 발생한 조건 하에 Event $E$가 발생할 확률이 바로 conditional probability임.$$p(E|F)=\dfrac{p(E,F)}{p(F)}$$조건에 의해, sample space가 변함. 조건에 의해 변화된 sample space에서의 확률을 구하는 것임.예제한 가족에서 두 아이들의 성별 맞추기가정 1. 각각의 아이가 딸이거나 아들일 확률은 0.5로 동일.가정 2. 둘째의 성별은 첫째의 성별과 independent.1) 두 아이가 모두 딸이 아닌 경우의 확률은? 2) 딸 한명과 아들 한명일 확률은? 3) 두 아이 모두 딸일 확률은?각각 1/4, 1/2, 1/4전체 경우를 따져보면 다음과 같기 때문임.(M,M), ..
[Math] Dependent & Independent (확률에서)
Dependent & Independent event $E$와 event $F$가 서로 independent 라면(~ independent events), 이 두 event가 동시에 선택될(발생될) 확률은 다음과 같음. $$ p(E,F) = p(E)p(F) $$ independent events의 경우, 각 사건의 발생 여부가 다른 사건의 발생 여부에 어떠한 영향을 주지 않는 것을 의미함. 동전 던지기(이상적 동전 사용)에서 4번 연속 Head가 나왔다고 할 때, 5번째 시도에서 head가 나올 확률은? 1/2 ← 각 사건이 독립임. 2개의 동전을 동시에 던지는 경우에서, 한 동전이 head가 나온 경우 두 동전 모두 tail일 확률은 0임. 즉 두 동전이 모두 tail인 event는 한 동전의 head..
[Math] Probability 란: Probability, Odds, Likelihood
Probability란?어떠한 event(사건, 사상)의 공간(=sample space, 발생가능한 모든 sample로 구성된 set)에서특정 event(or sample의 set)가 선택될(발생할) 수 있는불확실성(uncertainity)을 수치적으로 나타낸 것.어떤 event가 일어날 수 있는 경우의 불확실성을 수치적으로 나타낸것 예를 들어 설명하면 다음과 같음.sample space(←event의 공간) : 주사위 던지기로 나올 수 있는 모든 결과들의 집합.event(or sample) : 주사위 던지기의 눈의 갯수 또는 event의 공간의 subset주사위 던지기에서 2 나오는 경우주사위 던지기에서 홀수가 나오는 경우.event E에 대한 probability (event $E$의 확률)를 다음과..

[Math] Variance and Standard Deviation: Measure of Dispersion
Variance and Standard Deviation: Measure of DispersionMeasure of Central Tendency, 즉 현재 sampel의 representation인 mean을 통해해당 sample의 모든 cases를 하나의 값으로 표현하는 경우,해당 representation이 sample의 각각의 cases를 얼마나 잘 기술하는지는해당 sample이 얼마나 중앙에 몰려있는지에 따라 결정됨.중앙에 몰려 있을수록 representation으로 mean의 의미가 커짐.만약 각 cases가 퍼져있는(spread, dispersion) 경우엔, mean으로 각각의 case를 예측하는 것이 쉽지 않음.때문에 sample에서 값의 분포(distribution)를 나타낼 때, 각각..
[LA] Linear Transformation
Transformation $\mathbb{R}^n$ (domain) 에서 $\mathbb{R}^m$ (codomain) 으로의 transformation (= function or mapping) $T$는 domain에 속하는 각각의 vector $\textbf{x}$를 codomain의 vector $T(\textbf{x})$에 대응시키는 규칙임. 이를 다음과 같이 표기함 $$T: \mathbb{R}^n \to \mathbb{R}^m$$ Transformation은 Function, System, Mapping, Model 등의 용어로 대체되거나 각각의 정의에 사용되는 경우가 많음. https://dsaint31.tistory.com/215 Function (함수) : 간략 정의 Function은 흔..
[LA] Determinant (행렬식)
Matrix는 일종의 Linear transform을 의미함. Linear transform을 의미하는 matrix 들 중에서, Square Matrix에서 구해지는 Determinant는 해당하는 Linear transform의 특성을 나타내는 scalar 임. square matrix가 의미하는 linear transform은 차원이 증가할 수 없음을 기억할 것. Determinant의 의미 Determinant가 의미하는 것은 크게 다음의 3가지임. Scale (or Volumne) Change. Determinant의 magnitude는 univectore들에 의한 n-dimentional unit volume이 Linear transform에 의해 얼마나 확대 또는 축소되는지를 나타냄. 0이 될..
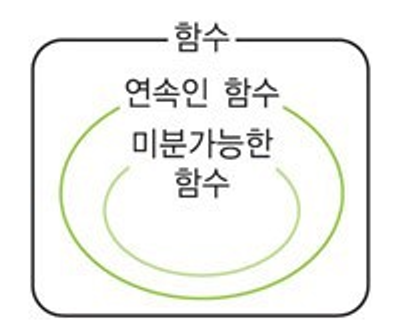
[Math] Continuous 와 Differentiable 의 관계
Differentiable and ContinuousFunction $f(x)$가 $x=a$에서 미분 가능 ($p$) 하면 $f(x)$는 연속이다($q$). (← implication, 조건명제)$p \implies q$ 는 참(True)이나 이의 역인 $q \implies p$는 거짓(False)임.Example$f(x)=|x|$ : $x=0$에서 continuous하지만 미분가능하지 않음.2023.06.22 - [.../Math] - [Math] Continuity (of Multivariate Function) and Contiguity0, \ \ \exists \delta>0 \mbox{ such that if } \mathbf x \in S \mbox{" data-og-host="dsaint31..
[Math] Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
다음이 기본적인 지수와 로그 함수의 도함수임. $$f(x)=e^x \rightarrow f^\prime(x)=e^x$$ $$f(x)=\log x \rightarrow f^\prime(x)=\frac{1}{x} $$ $$f(x)=a^x \rightarrow f^\prime(x)=a^x \log a$$ $$f(x)=\log_a x \rightarrow f^\prime(x)=\frac{1}{x\log a}$$ 2024.02.28 - [.../Math] - [Math] Limits of Log and Exponential Functions [Math] Limits of Log and Exponential Functions 대표적인 경우들은 다음과 같음. $$\underset{x\to 0}{\lim} \frac{..
[Math] Limits of Log and Exponential Functions
대표적인 경우들은 다음과 같음. $$\underset{x\to 0}{\lim} \frac{\log(1+x)}{x}=1$$ $$\underset{x\to 0}{\lim} \frac{\log_a(x+1)}{x} = \frac{1}{\log a}$$ $$\underset{x\to 0}{\lim} \frac{e^x -1}{x}=1$$ $$\underset{x\to 0}{\lim} \frac{a^x -1}{x}=\log a$$