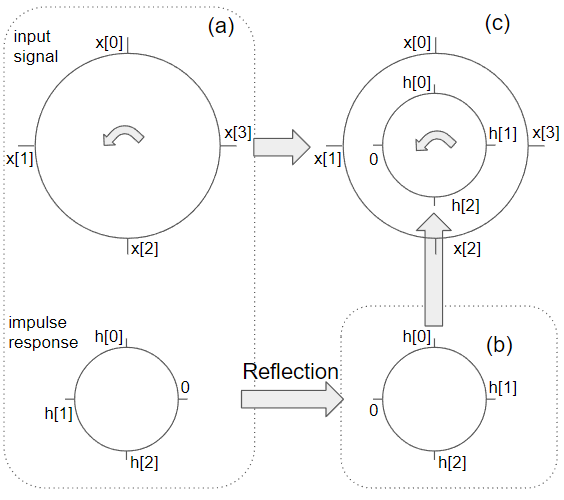
[SS] Circular Convolution
·
.../Signals and Systems
1. Circular Convolution이 필요한 이유.cyclic convolution이라고도 불림.DFT의 경우, frequency domain representation을 샘플링하므로, time domain representation도 periodic signal이 됨.때문에 DFT에서 time domain에서 input signal x[n]과 impulse response h[n]을 convolution하여 zero-state response y[n]를 구하는 경우, 기존의 (linear) convolution이 아닌 circular convolution으로 구해야 DFT의 sampling으로 인해 time domain의 x[n]과 h[n]이 주기를 가지고 반복되게 된 점을 반..
