[Math] Normal Distribution (정규분포)
·
.../Math
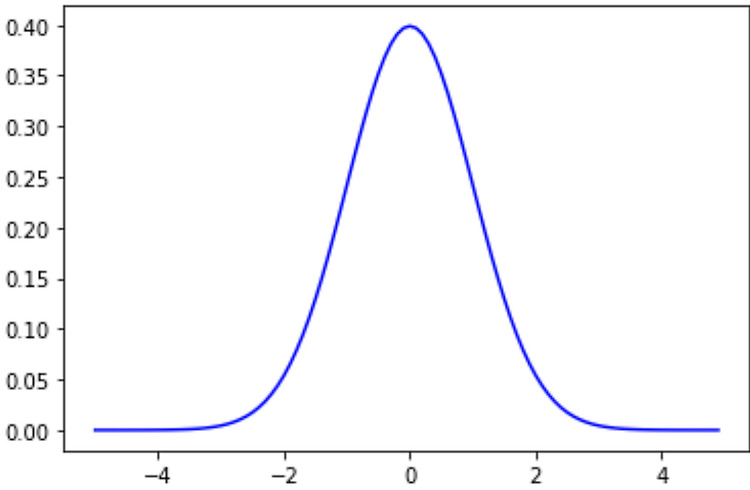
Normal DistirbutionGaussian Distribution, Laplace-Gaussian Distribution 라고도 불림.정의PDF는 다음과 같음. $$f(X)=\frac{1}{\sigma\sqrt{2\pi}}(e)^{-\frac{(X-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2}}$$$\mu$ : mean$\sigma$ : standard deviation PDF 이므로 probability를 다 더한 적분값은 1이 됨.$\mu$와 $\sigma$가 parameter인데, 이들이 0과 1인 경우 standard normal distribution (표준정규분포)라고 불림.일반 normal distribution에 z-Transform을 수행하면 standard normal distribution..