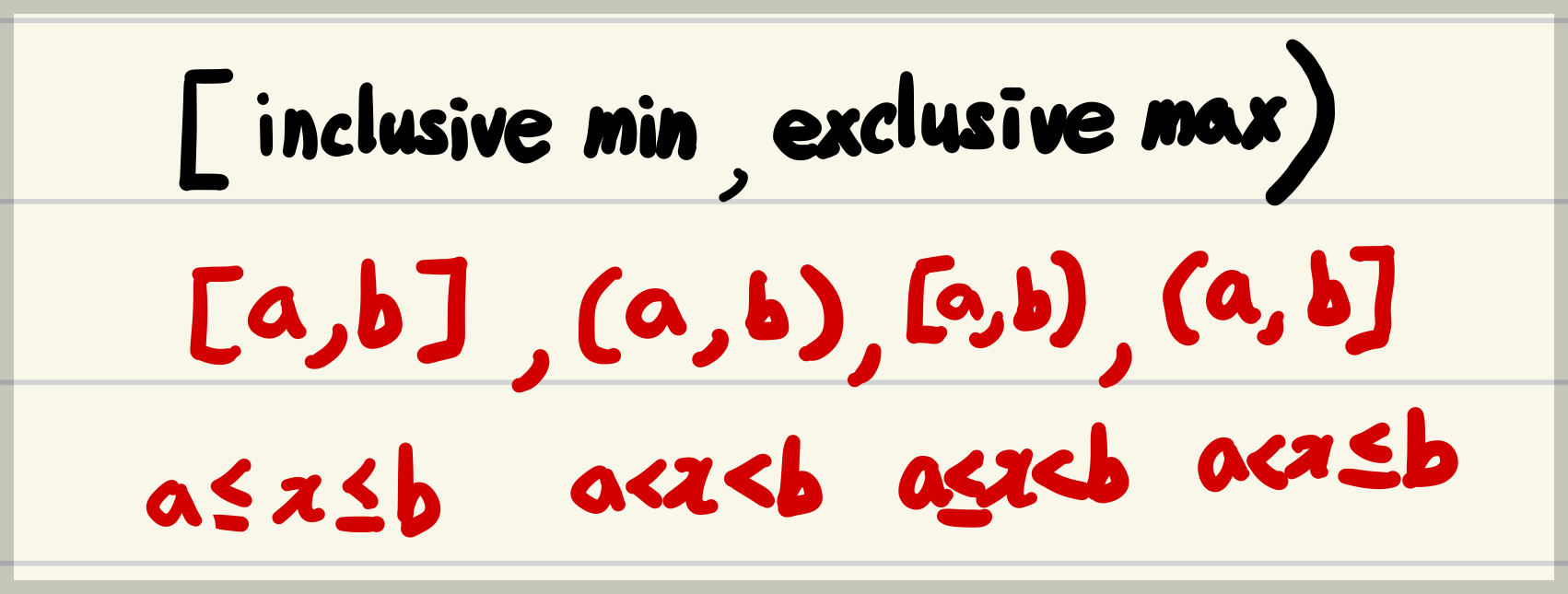
Definition
A (real) interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set.
구간(interval)을
parentheses와 square bracket을 이용하여 표현
하는 것을 꼭 기억할 것.
종류
An open interval (개구간) does not include its endpoints, and is indicated with parentheses.
For example,
- $(0,1)$ means greater than $0$ and less than $1$.
- This means $(0,1) = \{x | 0 < x < 1\}$.
A closed interval (폐구간) is an interval which includes all its limit points, and is denoted with square brackets.
For example,
- $[0,1]$ means greater than or equal to $0$ and less than or equal to $1$.
A half-open interval (반개구간=반폐구간) includes only one of its endpoints, and is denoted by mixing the notations for open and closed intervals.
For example,
- $(0,1]$ means greater than $0$ and less than or equal to $1$, while
- $[0,1)$ means greater than or equal to $0$ and less than $1$.
참고
- A degenerate interval (퇴화구간??) is any set consisting of a single real number (i.e., an interval of the form $[a,a]$).
- Some authors include the empty set in this definition.
- A real interval that is neither empty nor degenerate is said to be proper, and has infinitely many elements.
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Interval_(mathematics)
Interval (mathematics) - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia All numbers between two given numbers The addition x + a on the number line. All numbers greater than x and less than x + a fall within that open interval. In mathematics, a (real) interval is the set of all real numbe
en.wikipedia.org
https://dsaint31.github.io/math/math-week03/
[Math] Week 03
Limit and Continuity
dsaint31.github.io
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] Cauch’s Mean Value Theorem (1) | 2024.02.27 |
|---|---|
| [Math] Intermediate Value Theorem, Mean Value Theorem and Rolle’s Theorem (1) | 2024.02.27 |
| [Math] Limit of Scalar Function: Left-Sided Limit and Right-Sided Limit (0) | 2024.02.27 |
| [Math] Analytic Function (해석함수) (1) | 2024.02.26 |
| [Math] Inverse Function: Inverse vs. Reciprocal (0) | 2024.02.26 |