Euler Angle 과 Rotation Matrix
Euler Angle 은 3차원 공간에서 객체의 orientation 및 rotation(회전)을 표현하는데 사용되는 방법임.
- 참고로 orientation을 나타내는데 Axis Angle도 많이 사용되고,
- rotation(회전)의 경우는 Quaternion이 보다 많이 이용됨.
- 하지만, 가장 쉬운 표현법은 Euler Angle이라고 할 수 있음.
2023.08.05 - [.../Math] - [Math] Rotation Vector (= Axis-Angle, Rodrigues Angle)
[Math] Rotation Vector (= Axis-Angle, Rodrigues Angle)
3차원 공간에서의 rotation을 표현하는 방법.Euler angle과 함께 가장 많이 사용되는 방법 중 하나임.하지만 3개의 축에 대한 3개의 rotation angle로 표현하는 Euler angle과 달리,Rotation Vector는 하나의 vector
dsaint31.tistory.com
2024.07.09 - [.../Math] - [Math] Quaternion (사원수) 와 3D Rotation
[Math] Quaternion (사원수) 와 3D Rotation
1. Quaternion 이란?1843년 William Rowan Hamilton(아일랜드 수학자)이 제안한 수 (or 4D vector)로real number(실수) $1$과 세 개의 imaginary unit (허수 단위) $i, j, k$를 basis로 가지는4-dimenentional vector space(4차원 벡터
dsaint31.tistory.com
하지만, Euler Angle 은 3개의 축에 대한 회전각들로 구성되기 때문에 "순서"에 따른 다른 표기가 가능함.
일반적인 Euler Angle이
채택하는 순서는
Z-Y-X (Yaw-Pitch-Roll)임.
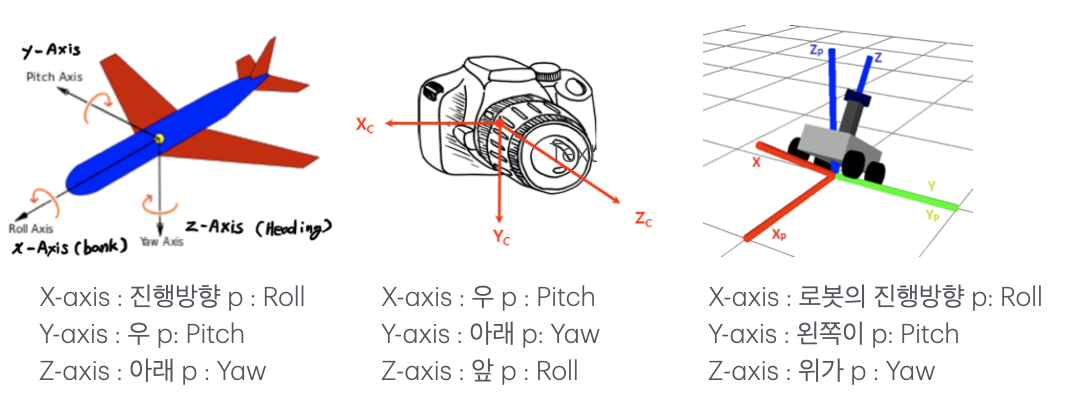
하지만, Camera의 pose (position + orientation) 등을 얻기 위해 이용되는
OpenCV의 cv2.decomposeProjectionMatrix 함수에서 반환되는 Euler Angle (Fixed Angle이라는 용어를 개인적으로 선호)은 Extrinsic X-Y-Z (Roll-Pitch-Yaw, sxyz) 순 임.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54336927/opencv-decompose-projection-matrix-euler-angle-wrong-direction(공식문서등에선 해당언급 찾기 어려움... --;;)
일부 문헌에서는 Intrinsic Rotation(or Rotated Rotation)에 한정하여
Euler Angle이라고 부르고, Extrinsic Rotation은 Fixed Angle이라고 부름.
이 문서에서는 Extrinsic Euler Angle Rotation을 Euler Angle이라고 언급함.
즉, Euler Angle의 일반적인 순서는 12가지(intrinsic 과 extrinsic의 구분을 안하고도)나 되므로 이에 대한 확인이 꼭 필요함.
아래의 설명은 Extrinsic Rotation (or static이라고도 불림)을 기준으로 진행됨.
2024.07.07 - [Programming/DIP] - [CV] Intrinsic Rotation and Extrinsic Rotation
[CV] Intrinsic Rotation and Extrinsic Rotation (Euler-Angle)
Intrinsic Rotation (내재적 회전)-Euler Angle RotationIntrinsic Rotation은 회전하는 객체의 고유한 좌표계를 기준으로 rotation이 이루어지는 방식(좌표계가 회전함)임. 각 rotation이 수행된 후, 다음 rotation은 이
dsaint31.tistory.com
많이 사용되는 Euler Angle 순서: Z-Y-X (Yaw-Pitch-Roll)
일반적인 오일러 각 순서, 즉 Z-Y-X 또는 Yaw-Pitch-Roll은 벡터에 회전을 적용하는 순서를 나타냄.
회전은 다음 순서로 적용됨.
- Z축 회전 (Yaw, $\alpha$ or $\psi$): 이 회전은 Z축을 중심으로 발생함.
- Y축 회전 (Pitch, $\beta$ or $\theta$): 이 회전은 Y축을 중심으로 발생함.
- X축 회전 (Roll, $\gamma$ or $\phi$): 이 회전은 X축을 중심으로 발생함.
여기서 각 rotation matrix는 다음과 같이 정의(Extrinsic 기준임)됨:
1. Z축 회전 (Yaw or Heading, $\alpha$ or $\psi$):
$$R_z(\alpha) = \begin{bmatrix}
\cos(\alpha) & -\sin(\alpha) & 0 \\
\sin(\alpha) & \cos(\alpha) & 0 \\
0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
2. Y축 회전 (Pitch, $\beta$ or $\theta$):
$$R_y(\beta) = \begin{bmatrix}
\cos(\beta) & 0 & \sin(\beta) \\
0 & 1 & 0 \\
-\sin(\beta) & 0 & \cos(\beta)
\end{bmatrix}$$
3. X축 회전 (Roll or Bank, $\gamma$ or $\phi$):
$$ R_x(\gamma) = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 0 & 0 \\
0 & \cos(\gamma) & -\sin(\gamma) \\
0 & \sin(\gamma) & \cos(\gamma)
\end{bmatrix}$$
vector가 rotation matrix뒤에 위치할 때 일반적인 Extrinsic Euler Angle 순서에 대한 행렬 곱셈 순서는 다음과 같음.
$$\mathbf{v}' = R_x(\gamma) R_y(\beta) R_z(\alpha) \mathbf{v} $$
여기서:
- $\mathbf{v}'$ 는 변환된 벡터임.
- $\mathbf{v}$ 는 원래 벡터임.
- $R_x$, $R_y$, $R_z$는 각각 X, Y, Z 축에 대한 회전 행렬임.
최종 roation matrix는 다음과 같음.
$$R_x R_y R_z = \begin{pmatrix}
\cos(\beta)\cos(\alpha) & -\cos(\beta)\sin(\alpha) & \sin(\beta) \\
\cos(\gamma)\sin(\alpha) + \sin(\gamma)\sin(\beta)\cos(\alpha) & \cos(\gamma)\cos(\alpha) - \sin(\gamma)\sin(\beta)\sin(\alpha) & -\sin(\gamma)\cos(\beta) \\
\sin(\gamma)\sin(\alpha) - \cos(\gamma)\sin(\beta)\cos(\alpha) & \sin(\gamma)\cos(\alpha) + \cos(\gamma)\sin(\beta)\sin(\alpha) & \cos(\gamma)\cos(\beta)
\end{pmatrix}$$
OpenCV의 cv2.decomposeProjectionMatrix 함수
OpenCV의 cv2.decomposeProjectionMatrix 함수에서
반환되는 Euler Angle 은 Extrinsic X-Y-Z (Roll-Pitch-Yaw) 순서를 따름.
회전은 다음 순서로 적용됨.
- X축 회전 (Roll or Bank, $\gamma$ or $\phi$): 첫 번째 회전임.
- Y축 회전 (Pitch, $\beta$ or $\theta$): 두 번째 회전임.
- Z축 회전 (Yaw or Heading, $\alpha$ or $\psi$): 세 번째 회전임.
따라서 vector가 matrix 뒤에 위치할 때 X-Y-Z Euler Angle 순서에 대한 행렬 곱셈 순서는 다음과 같음.
$$\mathbf{v}' = R_z(\alpha) R_y(\beta) R_x(\gamma) \mathbf{v}$$
최종행렬은 다음과 같음.
$$R_z R_y R_x = \begin{pmatrix}
\cos(\alpha)\cos(\beta) & \cos(\alpha)\sin(\beta)\sin(\gamma) - \sin(\alpha)\cos(\gamma) & \cos(\alpha)\sin(\beta)\cos(\gamma) + \sin(\alpha)\sin(\gamma) \\
\sin(\alpha)\cos(\beta) & \sin(\alpha)\sin(\beta)\sin(\gamma) + \cos(\alpha)\cos(\gamma) & \sin(\alpha)\sin(\beta)\cos(\gamma) - \cos(\alpha)\sin(\gamma) \\
-\sin(\beta) & \cos(\beta)\sin(\gamma) & \cos(\beta)\cos(\gamma)
\end{pmatrix}$$
요약 (Extrinsic 기준)
다음의 표를 참고.
| 순서 | 회전 순서 | 행렬 곱셈 순서 (벡터가 행렬 뒤에 있을 때) |
| Z-Y-X (Yaw-Pitch-Roll) | 1. Z축, 2. Y축, 3. X축 | $R_x R_y R_z \mathbf{v}$ |
| X-Y-Z (Roll-Pitch-Yaw) | 1. X축, 2. Y축, 3. Z축 | $R_z R_y R_x \mathbf{v}$ |
- 기본적으로 오일러 각의 순서는 Z-Y-X (Yaw-Pitch-Roll)임.
Euler Angle에서 추가 고려 사항
- 짐벌 락(Gimbal Lock):
- 여러 세트의 Euler Angle이 동일한 방향을 나타낼 수 있음.
- Gimbal은 Euler Angle을 물리적으로 구현하는 중첩된 회전고리들을 의미.
- Gibal Lock은 회전고리 2개가 동일한 평면에 일치하게 놓여서 한 축의 자유도가 사라지게 되는 물리적인 현상을 가리킴.
- 짐벌 락에 대한 자세한 정보
- 특이점(Singularity):
- 회전 각 중 하나가 90도에 가까워질 때 Euler Angle은 특이점이 발생할 수 있음.
- singularity란 특정 회전각부근에서 동일한 회전을 나타낼 수 있는 여러 Euler Angle의 해가 생겨 수치적 불안정성과 모호성이 발생하는 것을 가리킴.
- 해가 여러개 이다보니 약간의 회전의 변화가 Euler Angle에서 discontinuity 를 유발하게 됨.
주의 사항
- 벡터가 행렬 뒤에서 위치하여 곱해지는 경우, rotation matrix 들은 항상 역순으로 곱셈(Extrinsic의 경우 한정)해야 함.
- 벡터가 행렬 앞에 있을 때는 행렬간의 곱의 순서가 바뀜.
같이 읽어보면 좋은 자료들
2024.07.07 - [Programming/DIP] - [CV] Intrinsic Rotation and Extrinsic Rotation (Euler-Angle)
[CV] Intrinsic Rotation and Extrinsic Rotation (Euler-Angle)
Intrinsic Rotation (내재적 회전)-Euler Angle RotationIntrinsic Rotation은 회전하는 객체의 고유한 좌표계를 기준으로 rotation이 이루어지는 방식(좌표계가 회전함)임. 각 rotation이 수행된 후, 다음 rotation은 이
dsaint31.tistory.com
2023.08.05 - [.../Math] - [Math] Rotation Vector (= Axis-Angle, Rodrigues Angle)
[Math] Rotation Vector (= Axis-Angle, Rodrigues Angle)
Rodrigues Angle은 3차원 공간에서의 rotation을 표현하는 방법 중 하나임. Euler angle과 함께 가장 많이 사용되는 방법 중 하나임.하지만 3개의 축에 대한 3개의 rotation angle로 표현하는 Euler angle과 달리,Rot
dsaint31.tistory.com
Euler angles - Wikipedia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Description of the orientation of a rigid body Classic Euler angles geometrical definition. Fixed coordinate system (x, y, z) Rotated coordinate system (X, Y, Z) The Euler angles are three angles introduced by
en.wikipedia.org
OpenCV cv2.decomposeProjectionMatrix 함수 공식 문서
OpenCV: Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction
enum { cv::LMEDS = 4, cv::RANSAC = 8, cv::RHO = 16 } type of the robust estimation algorithm More... enum { cv::CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH = 1, cv::CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE = 2, cv::CALIB_CB_FILTER_QUADS = 4, cv::CALIB_CB_
docs.opencv.org
https://dlemrcnd.tistory.com/84?utm_source=chatgpt.com
DirectX11 - Fixed Angle(고정 각), Euler Angle(오일러 각), Quaternion(사원수) 정리
3D Rotation Matrix 회전 행렬은 회전 변환 관계를 나타내기 위한 행렬이다. https://dlemrcnd.tistory.com/2?category=515796 DirectX11 3D - 이동 행렬, 신축 행렬(스케일), 회전 행렬 1. 이동 행렬 (Translation Matrix) (x,y,z)
dlemrcnd.tistory.com
'Programming > DIP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [CV] Pose: Position + Orientation (+Boundary) (0) | 2024.07.09 |
|---|---|
| [CV] Intrinsic Rotation and Extrinsic Rotation (Euler-Angle) (0) | 2024.07.07 |
| [CV] Perspective Projection (원근 투영법): Camera to Image (0) | 2024.07.06 |
| [CV] Image Plane to Image Sensor Mapping (0) | 2024.07.06 |
| [CV] Triangulation: Simple Version (1) | 2024.07.04 |