Lagrange Method or Lagrange Multiplier Method
Lagrange Method (or Lagrange multiplier method, 라그랑지 승수법)은
equality constraints를 가진 optimization problem의 solution을 쉽게 구하는 방법을 가르킨다.
이를 좀 더 자세히 애기하면,
- equality constraint를 1개 이상을 가지는 optimization problem을
- non-constraint의 optimization problem의 형태로 바꾸어주어
- 훨씬 쉽게 optimal solution을 구하게 해준다.
엄밀히 애기하면,
optimal solution이 되기 위한 necessary condition을 이용하기 때문에
반드시 구한다고 할 수는 없다.
대상 : Optimization Problem with Equality Constraints
Lagrange Method로 푸는 Optimization은 다음과 같음.
$$\text{maxmize or minimize} f(\textbf{x})$$
subject to (s.t.)
- $g_1 (\textbf{x}) = 0$
- $\vdots$
- $g_n (\textbf{x}) = 0$
위의 정의에서
- $f(\textbf{x})$는 differentiable인 multi-variable function 임.
- $f:\mathbb{R}^n\to\mathbb{R}$.
$g_i(\textbf{x})=c_i$도 equality condition이지만,
표기를 쉽게 하기위해 이를
$g^\text{new}_i(\textbf{x})=g_i(\textbf{x})-c_i$라고 바꾸어서 처리하는 것을 가정한다.
inequality constraint들이 추가된 경우를 다루기 위해,
KKT 조건을 도입하여 확장 가능함.
확장된 Lagrange Method: 2023.07.06 - [.../Math] - [Math] Lagrangian from Standard Form using Indicator Function
[Math] Lagrangian from Standard Form using Indicator Function
Standard Form of Optimization ProblemEquailty constraints와 Ineqaulity contraints를 가지고 있는Optimization Problem (minimization의 경우)은 다음과 같이 표현된다. $$\begin{aligned}&\text{minimize }f(\textbf{x})\\ & \text{s.t:}\\ & g_i(\
dsaint31.tistory.com
참고
대부분의 optimization problem에서
$f(\textbf{x})$ 와 $g_i(\textbf{x})$ 들 모두
- continuous이고
- smooth 한 function이라는 것을
기본적으로 가정하고 있는 경우가 대부분이다.
이는 gradient를 기반으로 하는 방법(달리 말하면 미분을 기반으로 하는 방법)을 사용하기 위해서임.
참고로, smooth function이란 derivative를 무한차수로 구할 수 있는 함수를 의미한다.
[Math] Importance of Continuous and Smooth Functions in Optimization Problems
Continuous and Smooth FunctionOptimization에서 objective function과 constraint functions은 일반적으로 continuous 이면서smooth function (= 무한차수의 derivative를 구할 수 있는 function)임.Optimization이 statonarity 와 gradient
dsaint31.tistory.com
2023.06.22 - [.../Math] - [Math] Continuity (of Multivariate Function) and Contiguity
[Math] Continuity (of Multivariate Function) and Contiguity
Continuity (연속) 이란 If $S\subseteq \mathbb{R}^n$, then a function $f:S\to \mathbb{R}$ is continuous at $\textbf{a} \in S$ if $$\begin{equation}\label{cont.def} \forall \varepsilon >0, \ \ \exists \delta>0 \mbox{ such that if } \mathbf x \in S \mbox{
dsaint31.tistory.com
Key Idea.
Lagrange method는
구하고자 하는 solution을 $\textbf{x}^*$ 이라고 할 경우,
이 solution은 $f(\textbf{x})$와 $g_i(\textbf{x})$들의 선형조합의 contour lines(or planes)가 접하는 곳에 존재한다는 점을 이용한다 (둘 다 성립해야하므로).
tangent vector와 gradient는
항상 orthogonal인 것을 잊지 말자.
즉, 다음과 같은 Tangency Condition이 solution $\textbf{x}^*$에서 성립함.
Tangency Condition
$$\nabla f(\textbf{x}^*) = \sum_i^n \lambda_i \nabla g_i (\textbf{x}^*)$$
- $\lambda_i$는 각 equality condition에 따라 주어지며
- 이들은 위 식의 좌우변의 gradient의 크기들로 결정되는 비율에 해당함.
- 이들을 Lagrange Multipliers (라그랑지 승수)라고 부름.
- inequality constraints 까지 일반화된 형태에서는 dual variable 이라고도 불림
- 많은 경우, Lagrangian에 대한 dual problem으로 바꾸어 풀기 때문.
위 식은, object function과 equality condition 들의 선형조합의 contour lines가 접하는 경우,
각각의 gradient들이 평행하다 (같은 방향이거나 정반대 방향)는 점을 이용하고 있음.
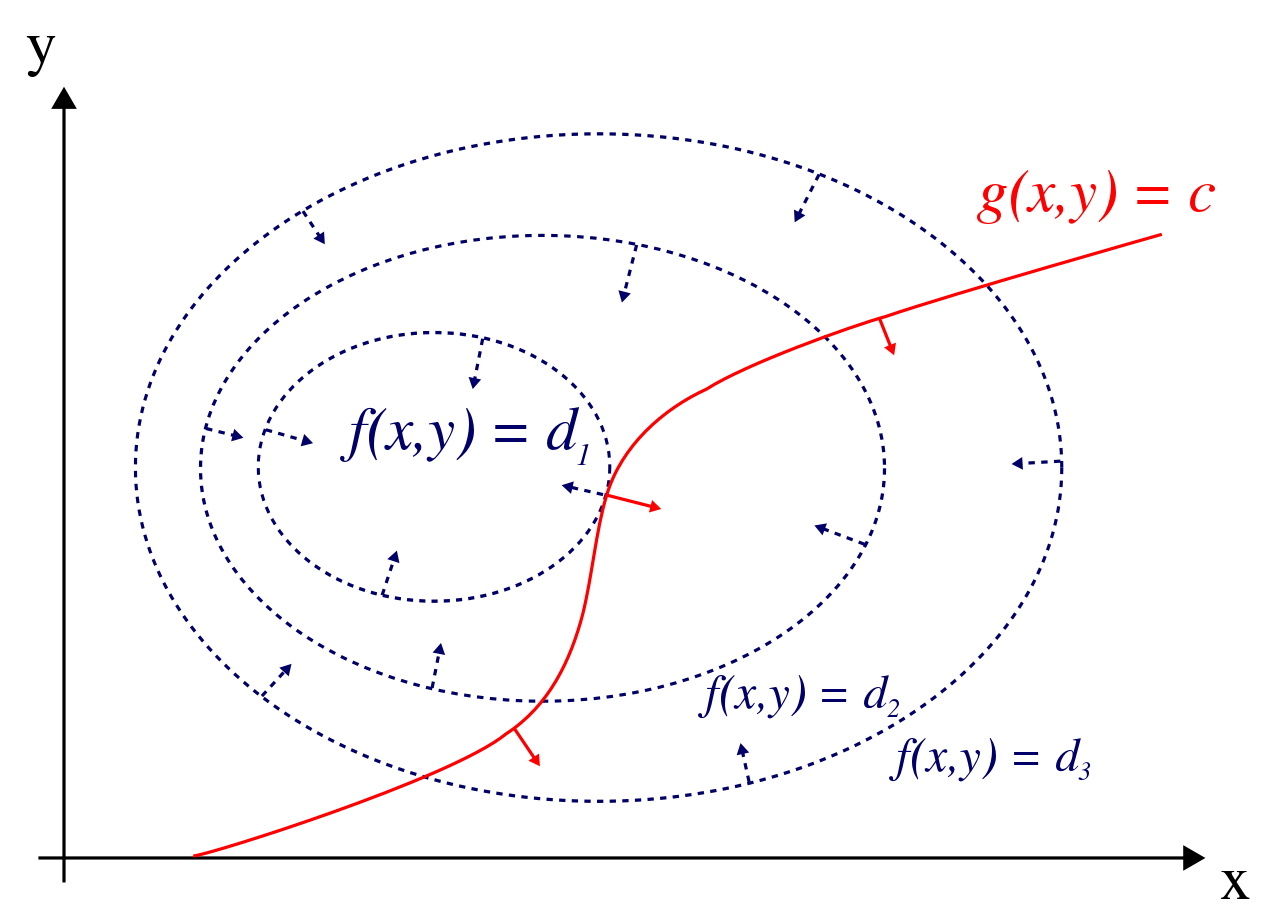
이는 필요조건이기 때문에,
solution $\textbf{x}^*$에서 위의 조건이 항상 성립하지만,
위의 조건이 성립한다고 반드시 solution인 건 아님.
2024.06.19 - [.../Math] - [Math] Ex: Lagrange Method: Tangency Condition
[Math] Ex: Lagrange Method: Tangency Condition
Lagrange method의 tangency condition에서gradient vectortangent vector의 이해를 돕는 example이 예제는 Lagrange 방법의tangency condition이어떻게 gradient vector와 tangent vector의 관계를 통해optimal solution(or optimal point)를
dsaint31.tistory.com
Tangency Condition 외 만족해야하는 조건.
기본적으로 constraints를 만족해야 하므로, 다음이 반드시 성립함.
$$g_i(\textbf{x}^*)= 0 \text{ ,where }i=1, \dots, n$$
이를 vector로 표현하면 다음과 같음.
$$\textbf{g}(\textbf{x}^*)=\begin{bmatrix}g_1(\textbf{x}^*) \\ \vdots \\ g_n(\textbf{x}^*)\end{bmatrix}=\textbf{0}$$
solution $\textbf{x}^*$이기 위한 필요 조건 : 두 개의 조건 합치기
위에서 다룬 tangency condtion을 바탕으로 다음과 같은 constraints가 없는 식을 구할 수 있음.
$$L (\textbf{x}, \boldsymbol{\lambda} ) = f(\textbf{x}) - \boldsymbol{\lambda} \cdot \textbf{g}(\textbf{x})$$
- 위의 $L$을 Lagrangian이라고 부르며,
- 이는 기존의 constraints들과 $f$를 합쳐서 constraint가 없는 형태로 바꾼 것이다.
참고: 사실 tangency condition을 이용할 때, $\lambda$의 sign에 따라 다음으로도 표시 가능함.
(사실 아래의 경우를 더 많이 사용.)
$$L (\textbf{x}, \lambda) = f(\textbf{x}) + \boldsymbol{\lambda} \cdot \textbf{g}(\textbf{x})$$
solution $\textbf{x}^*$에서는 Lagrangian의 gradient가 항상 zero vector가 되게 하는 $\boldsymbol{\lambda}^*$ vector가 존재한다.
즉, 다음이 성립하는 $\boldsymbol{\lambda}^*$ vector가 존재.
$$\nabla L (\textbf{x}^*, \boldsymbol{\lambda}^* ) = \textbf{0}\quad \leftarrow\text{Zero Vector}$$
동시에 $\textbf{x}^*$는 feasible set에 속하므로 다음도 성립함.
$$\textbf{g}(\textbf{x}^*)=\textbf{0}\quad \leftarrow\text{Zero Vector}$$
간단히 말해서 solution $\textbf{x}^*$는 반드시 위의 두 조건을 모두 만족해야만 한다.
- 즉, 이 두 조건은 solution $\textbf{x}^*$가 되기위한 necesarry condition임.
- 아쉽게도 sufficient condtion이 아님
이 두 개의 조건이 necessary condition(필요조건)이 되는 경우는,
Regularity conditions (=constraints qualifications) 이 성립하는 경우임.
Optimization problem에서
Regularity conditions를 만족하는 solution $\textbf{x}^*$ 는
항상 Lagrangian에서의 stationary point(정류점, or critical point)이라는,
solution $\textbf{x}^*$의 necessary condition에 기반하여
solution을 구하는 것이 Lagrange method의 핵심임.
2023.07.07 - [.../Math] - [Math] A regular point of the feasible set.
[Math] A regular point of the feasible set.
Regular Points (정규점)Consider the constrained optimization problem of minimizing $f(\textbf{x})$ subject to the constraints $h_i(\textbf{x})=0, i=1 \text { to } p$. A point $\textbf{x}^*$ satisfying the constraints is said to be a regular point (정
dsaint31.tistory.com
2023.07.10 - [.../Math] - [Math] Stationary point (or Critical point)
[Math] Stationary point (or Critical point)
Stationary point (or Critical point, 정류점)(Convex) Opimization에서 찾고자하는 solution은 objective function에 대한 local minimum이다.이를 곧바로 찾기는 쉽지 않기 때문에, solution이 될 수 있는 후보들을 먼저 gradie
dsaint31.tistory.com
Lagrange Method
- Step 1: Introduce a new vector $\lambda$, and define a new function $L$ as follows:
This function $L$ is called the “Lagrangian”, and
the new variable $\lambda$ is referred to as a “Lagrange multiplier”vector
$$
L(\textbf{x},\lambda)=f(\textbf{x})-\lambda \cdot (g(\textbf{x}))
$$
- Step 2: Set the gradient of $L$ equal to the zero vector.
In other words, find the critical points of $L$.
$$
\nabla L(\textbf{x}, \lambda)=\textbf{0} \quad \leftarrow\text{Zero Vector}
$$
- Step 3: Consider each solution, which will look something like $(\textbf{x}_0, \lambda_0))$.
Plug each one into $f$.
Or rather, first remove the $\lambda_0$ component, then plug it into $f$, since $f$ does not have $\lambda$as an input. Whichever one gives the greatest (or smallest) value is the maximum (or minimum) point your are seeking.
2024.06.19 - [.../Math] - [Math] Example of Lagrange Method
[Math] Example of Lagrange Method
Example 1 :$x$, $y$ 가 조건 $g(x,y)=2x−y−10=0$을 만족할 때, $f=x^2+y^2$의 global minimum(최솟값)을 구하라.Lagrangian$L=x^2+y^2+\lambda (2x-y-10)$풀이Tangency condition 에 의해 최솟값을 가지는 $x,y$에서 다음이 성립.$\d
dsaint31.tistory.com
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] Lagrangian Primal and Lagrangian Dual (0) | 2023.07.05 |
|---|---|
| [Math] Upper Bound (상계) and Lower Bound (하계) (0) | 2023.07.05 |
| [Math] Tangent Vector (0) | 2023.06.24 |
| [Math] Chain Rule (연쇄법칙) (0) | 2023.06.24 |
| [Math] Gradient (구배, 기울기, 경사, 경도) Vector (0) | 2023.06.24 |