Standard form of Optimization Problem
Equailty constraints와 Ineqaulity contraints를 가지고 있는 optimization problem (minimization의 경우)은 다음과 같이 표현된다.
$$\begin{aligned}&\text{minimize }f(\textbf{x})\\
& \text{s.t:}\\ & g_i(\textbf{x}) \le 0, i=1,\dots,m \\ & h_j(\textbf{x})=0,j=1,\dots,k\end{aligned}$$
여기서 $f: \mathbb{R}^n \to \mathbb{R}$ 임.
이 standard form 의 optimization problem을 가르켜,
원래 풀어야하는 문제라는 뜻에서 Primal problem이라고도 부름.
convex problem으로 한정되지는 않으나,
convex problem일 경우 여러가지로 풀기 쉬어지는 장점을 가지기 때문에
대부분 convex problem으로 한정된다.
Lagrangian Primal
위 optimization problem에 대한 Lagrangian (or Lagrangian primal)은 다음과 같이 정의됨.
$$L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})=f(\textbf{x})+\boldsymbol{\alpha}\cdot\textbf{g}(\textbf{x})+\boldsymbol{\mu}\cdot\textbf{h(x)}$$
다음으로 풀어서 표기할 수 있음.
$$L(\mathbf{x}, \boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})=f(\mathbf{x})+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \alpha_i g_i(\mathbf{x}) +\sum_{j=1}^{k} \mu_j h_j(\mathbf{x})$$
여기서 $\boldsymbol{\alpha} \in \mathbb{R}^m$ 이고 $\boldsymbol{\mu} \in \mathbb{R}^k$이므로,
$$L: \mathbb{R}^n \times \mathbb{R}^m \times \mathbb{R}^k \to \mathbb{R}$$
Lagrangian을 통해,
contraint optimzation problem이
unconstrained optimization problem이 됨.
Lagrangian Primal이 위와 같이 나오는 것에 대한 보다 자세한 설명은 다음 URL을 참고할 것.
2023.06.26 - [.../Math] - [Math] Lagrange Method or Lagrange Multiplier Method
[Math] Lagrange Method or Lagrange Multiplier Method
Lagrange Method or Lagrange Multiplier MethodLagrange Method (or Lagrange multiplier method, 라그랑지 승수법)은equality constraints를 가진 optimization problem의 solution을 쉽게 구하는 방법을 가르킨다. 이를 좀 더 자세
dsaint31.tistory.com
2023.07.06 - [.../Math] - [Math] Lagrangian from Standard Form using Indicator Function
[Math] Lagrangian from Standard Form using Indicator Function
Standard Form of Optimization ProblemEquailty constraints와 Ineqaulity contraints를 가지고 있는Optimization Problem (minimization의 경우)은 다음과 같이 표현된다. $$\begin{aligned}&\text{minimize }f(\textbf{x})\\ & \text{s.t:}\\ & g_i(\
dsaint31.tistory.com
Lagrangian dual로의 확장
Lagrangian primal의 중요한 특성 중 하나는
$\boldsymbol{\alpha}$의 모든 component $\alpha_i \ge 0$일 경우
전체 feasible set $S$ 에 속하는 $\textbf{x} \in S$에서는
항상 primal problem의 optimal value $p^* \triangleq \underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min}}f(\textbf{x})$ 보다 항상 작거나 같다는 것임.
$$p^* \triangleq \underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }} f(\textbf{x}) \ge \underset{\textbf{x} \in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$$
$\textbf{x}$가 feasible set $S$에 속하는 것으로 제한될 때의 최소값인
$\underset{\textbf{x} \in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$에 비해,
모든 $\textbf{x}$로 확장한 경우의 Lagrangian primal의 최소값이 같거나 작은 것이 당연하므로 다음이 성립.
$$p^* \triangleq \underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }} f(\textbf{x}) \ge \underset{\textbf{x} \in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \ge \underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{min }}L (\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$$이 성립됨.
여기서 $\underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{min }}L (\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$ 은Lagrangian의 infimum (하한, 최대하계)을 의미함.
$$ \displaystyle \underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{inf}}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) = \underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{min }}L (\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$$
Lagrangian Dual
앞서 주어진 $L: \mathbb{R}^n \times \mathbb{R}^m \times \mathbb{R}^k \to \mathbb{R}$에 대한 Lagrangian dual function $d: \mathbb{R}^m \times \mathbb{R}^k \to \mathbb{R}$은 다음과 같이 정의됨.
$$\displaystyle D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})=\displaystyle \text{inf}_{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})=\underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{min }}L (\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})$$
즉, Lagrangian Dual은 Lagrangian Primal의 infimum(하한)임.

infimum에 대해선 다음을 참고: 2023.07.05 - [.../Math] - [Math] Upper Bound (상계) and Lower Bound (하계)
[Math] Upper Bound (상계) and Lower Bound (하계)
Upper Bound and Supremum Wolfram MathWorld에서 언급하는 Upper Bound (상계)와 Supremum(상한) 정의는 다음과 같음. A function $f$ is said to have an upper bound $c$ if $f(\textbf{x})\le c$ for all $\textbf{x}$ in its domain. The least upper
dsaint31.tistory.com
실제로 Lagrangian Dual에서
- $\textbf{x}$를 $\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}$의 식으로 치환을 하게 되며,
- 해당 치환은 $\displaystyle \frac{\partial L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})}{\partial \textbf{x}}=0$를 이용하여 구함.
2023.07.07 - [.../Math] - [Math] Duality (쌍대성) 이란 : Optimization에서
[Math] Duality (쌍대성) 이란 : Optimization에서
요약optimization에서 Duality 는 primal problem과 dual problem의 관계를 의미함.이를 이용하여,원래 최적화(minimization ro maximization)해야 할 문제인 primal problem을 직접 푸는 대신에,duality를 이용하여 이에 해
dsaint31.tistory.com
Lagrangian Dual과 Lower Boundary of $f(\textbf{x})$
Standard form으로 주어진 optimization proble의 solution을
$\textbf{x}^* \in \mathbb{R}^n$이라고 하고,
최솟값 $p^*=f(\textbf{x}^*)=\underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }}f(\textbf{x})$라고 하고,
$\boldsymbol{\alpha}$의 모든 component $\alpha_i \ge 0$인 경우,
Lagrange dual $D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})$는
$p^*$ ($f$의 optimal value)에 대해 infimum이 된다.
즉,
$$f(\textbf{x}) \ge f(\textbf{x}^*)=p^* \ge \underset{\textbf{x}\in\mathbb{R}^n}{\text{min }}L (\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})\ge D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})$$
모든 $\alpha_i$가 0 이상이면서
$\textbf{x}$가 feasible set $S$에 속할 경우 constraints를 만족하므로, 다음이 항상 성립.
- $$\underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \le f(\textbf{x})$$
- Lagrangian의 두번째 항이 항상 0이하로 나오고, 세번째 항은 0이 되기 때문임.
Lagrangian dual은 Lagrangian의 infmum이므로 다음이 성립함.
$$D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \le \underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \le p* = f(\textbf{x}^*) \le f(\textbf{x})$$
결국, 다음이 성립한다.
$$D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \le f(\textbf{x}^*)=p^*\quad \text{for }\forall \alpha_i \ge 0, \mu_j$$
위의 식에 의해,
$\text{max }D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}, \boldsymbol{\mu})$를 통해 얻은 optimal dual value $d^*=D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}^*, \boldsymbol{\mu}^*)$도 $p^*=f(\textbf{x}^*)$보다 작거나 같음이 성립함.
$$d^*=D(\boldsymbol{\alpha}^*, \boldsymbol{\mu}^*) \le p^*=f(\textbf{x}^*)$$
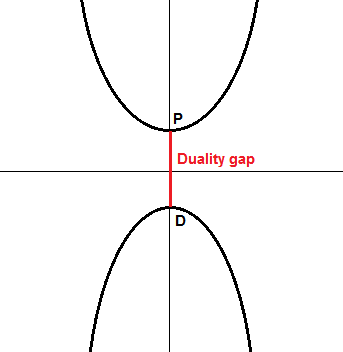
위의 관계를 가르켜 weak duality라고 칭함.
Lagragian Dual Problem
다음을 Primal Problem (standard form) 이라고 부름.
$$\begin{aligned}&\text{min }f(\textbf{x})\\
& \text{s.t:}\\ & g_i(\textbf{x}) \le 0, i=1,\dots,m \\ & h_j(\textbf{x})=0,j=1,\dots,k\end{aligned}$$
다음은 위의 Primal Problem에 대한 Lagrangian Problem임.
$$\underset{\textbf{x}\in S}{\text{min }}L(\textbf{x},\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) $$
- $\boldsymbol{\alpha}$의 모든 component $\alpha_i \ge 0$
다음은 위의 Primal Problem에 대한 Lagrangian Dual Problem임.
$$\begin{aligned}&\text{max }D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})\\& \text{s.t:}\\ & \alpha_i \ge 0, i=1,\dots,m\end{aligned}$$
Primal problem을 풀 때,
- Lagrangian을 이용하여 not-constrained problem으로 바꾸어 풀 수 있으며,
- 또는 Lagrangian dual problem으로 바꾸어 풀 수도 있다.
일반적으로 Dual Problem의 optimal solution(최적해)가 Primal Problem의 optimal solution(최적해)는 같지 않고 이들에서의 최적값들 $p^*, d^*$들도 같지 않다.
단지 weak duality에 의해 $p^* \ge d^*$ 가 성립한다.
하지만, $D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) \le f(\textbf{x}^*) \le f(\textbf{x})$ 이기 때문에 (weak duality),
만약 $D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}) = f(\textbf{x})$인 $\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu},\textbf{x}$가 존재한다면, 위의 weak duality에 의해 해당 $\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu},\textbf{x}$은 optimal solution이 된다 (strong duality).
즉, Strong duality의 경우 Dual Problem에서 구한 최대값 $d^*$은 Primal Problem의 최소값 $p^*$과 같아지며 이들 strong duality와 관련된 여러 conditions (Slater's condition, KKT conditions)을 활용하면 보다 효과적으로 풀 수 있게 된다.
일반적으로 dual problem을 이용하여 푸는 순서는 다음과 같음.
- $\nabla_\textbf{x} L = \textbf{0}$ 을 만족하는 $\textbf{x}$ 를 구함.
- $\nabla_{\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}} D(\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu})=\textbf{0}$으로 $\boldsymbol{\alpha},\boldsymbol{\mu}$를 구함.
Duality와 관련된 여러 conditions에 대한 이해가 이 문서에서의 Lagrangian과 Lagrangian Dual Problem에 더해지면 Optimization을 보다 효과적으로 풀 수 있게 된다.
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] Slater's Condition (0) | 2023.07.06 |
|---|---|
| [Math] Lagrangian from Standard Form using Indicator Function (0) | 2023.07.06 |
| [Math] Upper Bound (상계) and Lower Bound (하계) (0) | 2023.07.05 |
| [Math] Lagrange Method or Lagrange Multiplier Method (0) | 2023.06.26 |
| [Math] Tangent Vector (0) | 2023.06.24 |