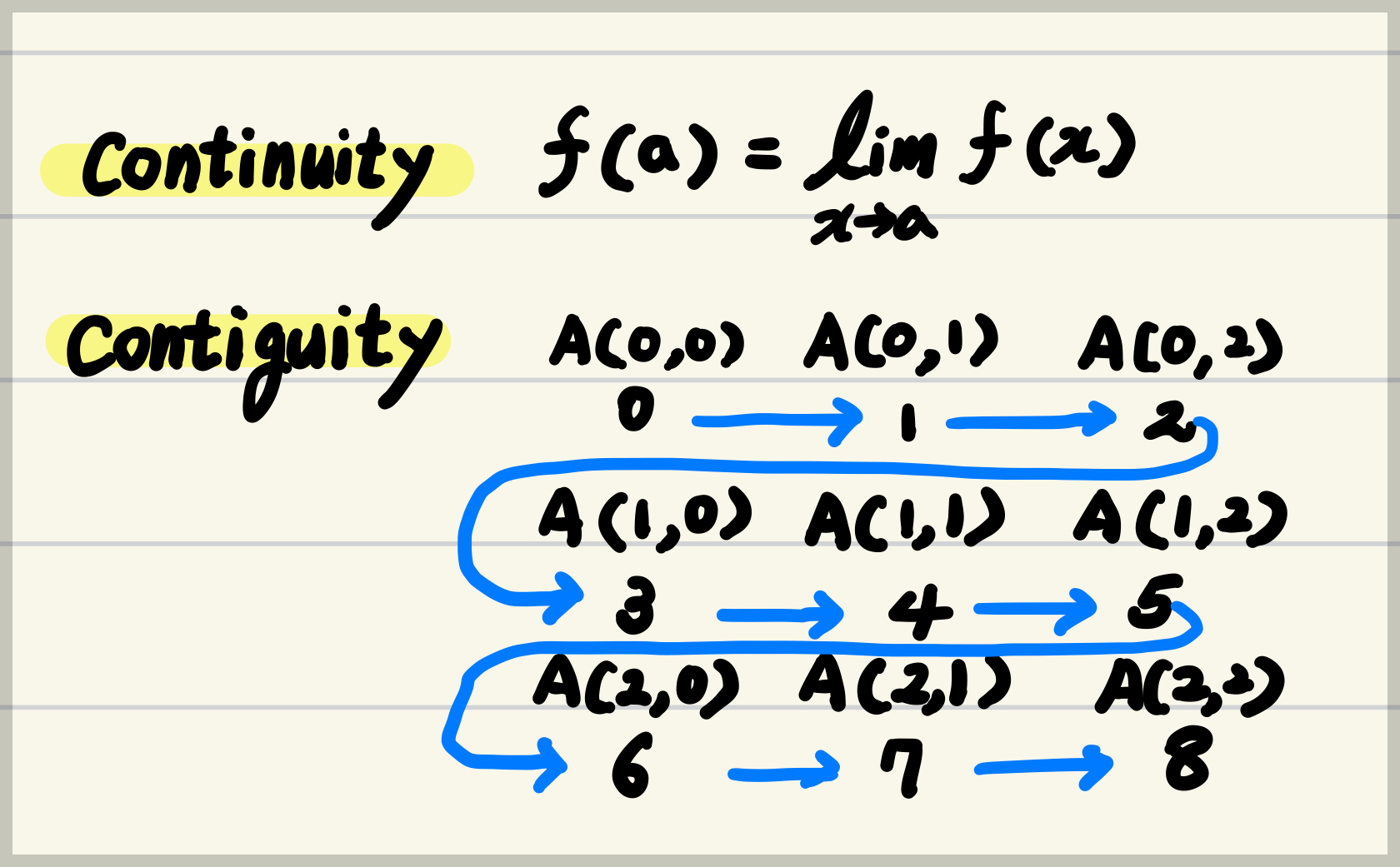
Continuity (연속) 이란
If $S\subseteq \mathbb{R}^n$, then a function $f:S\to \mathbb{R}$ is continuous at $\textbf{a} \in S$ if
$$\begin{equation}\label{cont.def}
\forall \varepsilon >0, \ \ \exists \delta>0 \mbox{ such that if } \mathbf x \in S \mbox{ and } |\mathbf x - \mathbf a|<\delta, \mbox { then } | f(\mathbf x) - f(\mathbf a)| < \varepsilon.
\end{equation}$$
만약 $f$가 모든 $S$의 point에서 continuous하다면, $f$ 는 연속함수(continuous function)임.
2024.02.27 - [.../Math] - [Math] interval (구간)
[Math] interval (구간)
DefinitionA (real) interval is a set of real numbers that contains all real numbers lying between any two numbers of the set.구간(interval)을 parentheses와 square bracket을 이용하여 표현하는 것을 꼭 기억할 것.종류An open interval (개
dsaint31.tistory.com
연속함수란,
정의역 $S \subseteq \mathbb{R}^n$ 위의 함수 $f:S \to \mathbb{R}$ 가
모든 점 $\mathbf{a} \in S$에서 $\varepsilon-\delta$ 조건을 만족하여,
입력이 연속적으로 변할 때 출력도 끊김 없이 연속적으로 변하는 함수이다.
Limit과 Continuity
limit으로 표현하면 다음이 성립함.
$f:S\to \mathbb{R}^n$ is continuous at $\textbf{a} \in S$ if and only if $\displaystyle\lim_{\mathbf x\to \mathbf a} f(\textbf{x}) = f(\textbf{a})$
만약 scalar function으로 한정하고 특정 위치 $x=a$에서 표현하면 다음과 같음.
특정위치 $x=a$에서 $f(x)$가 Continuous 이라면 다음을 만족(← Cauchy,1821)
- $\displaystyle \lim_{x\to a} f(x)$가 존재.
- $f(a)$가 존재.
- $\displaystyle \lim_{x \to a} f(x)=f(a)$가 성립.
Basic Properties of continuity
Multivariable Function $f(\textbf{x}),g(\textbf{x})$가 $\textbf{a}$에서 continuous라면, 다음의 function들도 $\textbf{a}$에서 continuous임.
- $f(\textbf{x}) \pm g(\textbf{x})$
- $cf(\textbf{x}) \text{ ,where }c \text{ is a constant.}$
- $f(\textbf{x})g(\textbf{x})$
- $\displaystyle \frac{f(\textbf{x})}{g(\textbf{x})} \text{, where } g(\text{a}) \ne 0$
쉽게 말하면 multivariable function의 continuity는 사칙연산과 scalar multiple에 대해 보존됨을 알 수 있음.
Continuous 와 Contiguous 의 차이.
- Continuous
- 수학, 물리학, 일상적 용어에서 사용
- 중단이나 간격 없이 끊임없이 이어지는 성질을 나타냄.
- 위의 수학적 정의를 가짐.
- Contiguous
- 주로 컴퓨터 메모리 또는 데이터 구조의 물리적 배치와 관련된 용어
- C 등에서 array 또는 tensor 를 나타내는 class 들이 storage를 위해 채택됨.
- 데이터가 메모리 상에서 서로 인접한 위치에 저장됨을 의미합니다.
같이보면 좋은 자료들
http://www.math.toronto.edu/courses/mat237y1/20199/notes/Chapter1/S1.2.html
1.2: Limits and Continuity
Our goal is to show that \[\begin{equation}\label{facta} \forall \varepsilon >0, \exists\delta>0 \mbox{ such that } 0<|x|< \delta \Rightarrow |f(x,mx) - L|<\varepsilon \end{equation}\] Our assumption is that \(\lim_{(x,y)\to (0,0)}f(x,y) = L\). This implie
www.math.toronto.edu
https://dsaint31.github.io/math/math-week03/
[Math] Week 03
Limit and Continuity
dsaint31.github.io
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] Differentiation (or Differential, 미분)과 Difference (차분) (0) | 2023.06.23 |
|---|---|
| [Math] Differentiability of MultivariableFunctions (0) | 2023.06.23 |
| [Math] Limit Laws of Multivariate Function (0) | 2023.06.22 |
| [Math] Limit of a Multi-Variate function and Limit Point (0) | 2023.06.22 |
| [Math] Level Set (0) | 2023.06.22 |