Projective Space
$n$ dimension의 real projective space $\mathbb{P}^n$는 다음과 같은 vector space 사에 정의된 quotient space (일종의 vector들의 집합)임.
$$\mathbb{P}^n = ( \mathbb{R}^{n+1} \setminus \{\mathbf{0}\} ) / \sim$$
- $\setminus$ 는 difference(차집합)을 의미. 원점(zero vector)을 뺀 것임.
- $/$ 는 quotient by 로 quotient space를 만드는 것.
- scalar mutiple equivalent calss $\sim$에 대한 quotient space임: $\textbf{x} ~\lambda \textbf{x}, \lambda \ne 0$
간략하게는 다음과 같이 표현하기도 함.
$$\mathbb{P}^n = \mathbb{R}^{n+1} - \mathbf{0} $$
Projective space는 정의상 vector space가 아님.
vector에서 magnitude를 빼고 direction만 남긴 벡터의 방향을 나타내는 공간임.
Duality
Projective space 에서는 duality가 성립하여,
- 해당 space에 속하는 element인 vector들은
- point 일수도 있고, line일수도 있음
- (point에서 성립하는 것은 line에서도 성립:duality)
2024.06.28 - [.../Math] - [Math] Duality of Projective Geometry
[Math] Duality of Projective Geometry
projective geometry(사영기하학)에서 duality(이중성) 는point(점)과 line(직선) 사이의 역할을 교환해도 성질이 변하지 않는 관계를 의미함 이 글은 projective geometry에서 duality(이중성)를 예를 통해 설명함.
dsaint31.tistory.com
Projective space 와 Affine space
Projective space는
- Affine space에
- parallel lines가 교차하는 one point at infinity (=ideal point) 가 추가된 것임.
예를 들어. $\mathbb{P}^2$는
- homogeneous coordinates로 표현될 때
- 3개의 elements를 가지는 vector 로서 표현되고,
아래와 같은 equivalent (동치관계: 아래에서 등호로 표시함)가 성립함
$$\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{bmatrix} = k\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{x}{z} \\ \frac{y}{z} \\ 1\end{bmatrix}$$
point and line
위의 homogeneous coordinates는 다음의 수식처럼
- $\mathbb{R}^2$의 point에 대응될 수 있고,
- $\mathbb{R}^2$의 line에 대응될 수 있음.
$$(x,y) \rightarrow \begin{bmatrix}x \\ y \\ 1\end{bmatrix}, ax+by+c=0 \rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} a \\ b \\ c \end{bmatrix}$$
2024.06.16 - [.../Math] - [Math] Homogeneous Coordinate and Projective Geometry
[Math] Homogeneous Coordinate and Projective Geometry
Homogeneous Coordinates (동차 좌표)와 Projective Geometry (사영 기하학)1. 개요1-1. Homogeneous Coordinates의 정의와 특성Homogeneous Coordinates (동차 좌표)는 Euclidean Coordinates (유클리드 좌표) 시스템을 확장하여 Proje
dsaint31.tistory.com
[CV] Intersection and Ideal Point; Homogeneous Coordinate and Cross Product
Intersection and Ideal Point이 글에서는 homogeneous coordinates(동차 좌표)와 cross product(교차곱)을 이용하여 두 직선의 교점을 찾는 방법을 다룸.또한, 평행한 직선의 경우에 ideal point(이상점)이 나오는 경우
dsaint31.tistory.com
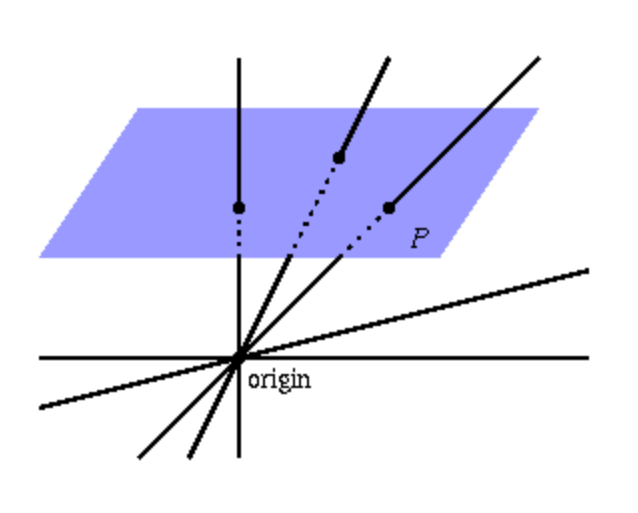
기하학적으로 살펴보기
기하학적으로 살펴보면,
- 2-Dimenstional Projective Space $\mathbb{P}^2$ 는 일종의 set이기 때문에,
- 이 set에 포함되는 element는 각각 다음 그림에서 origin(원점)을 제외한 line에 해당함.
- (각 line을 이루는 3차원의 점들은 $\mathbb{P}^2$에서 동치관계임: 해당 line으로 p에 투영.)
더 읽어보면 좋은 자료들
https://www.math.toronto.edu/mathnet/questionCorner/projective.html
Question Corner -- Understanding Projective Geometry
Euclid wrote down a list of these axioms: five of them (though actually there are some other axioms implicit in Euclid's definitions). He called them postulates. The first four postulates are so self-evident that they clearly ought to be satisfied by anyth
www.math.toronto.edu
다중관점기하학(Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision) 책 내용 정리 Part 1
Youtube 다중관점기하학(Multiple View Geometry) 개념 정리 www.youtube.com0. Projective Space사영 공간(projective space) $\mathbb{P}^{n}$는 $\mathbb{R}^{n+1}$ 공간 상의 원점을 지나는 직선들의 집합을 의미한다. 따라서
alida.tistory.com
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] Term: Algebra란? (대수란?) (1) | 2024.07.20 |
|---|---|
| [Math] Quaternion (사원수) 와 3D Rotation (0) | 2024.07.09 |
| [Math] Hypothesis Testing 에서 Conservative Approach (보수적 접근법)란? (1) | 2024.07.05 |
| [Math] Duality of Projective Geometry (0) | 2024.06.28 |
| [ML] Out of Bag: 유도하기. (0) | 2024.06.20 |