1847년 독일의 물리학자 Gaustav R. Krichhoff가 정립한 법칙.
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL, 1법칙)
Kirchhoff's Current Law or KCL, states that
“the total current or charge entering a junction or node is exactly equal to the charge leaving the node as it has no other place to go except to leave, as no charge is lost within the node“.
In other words the algebraic sum of ALL the currents entering and leaving a node must be equal to zero,
$$I(\text{exiting}) + I(\text{entering}) = 0$$.
This idea by Kirchhoff is commonly known as the Conservation of Charge.
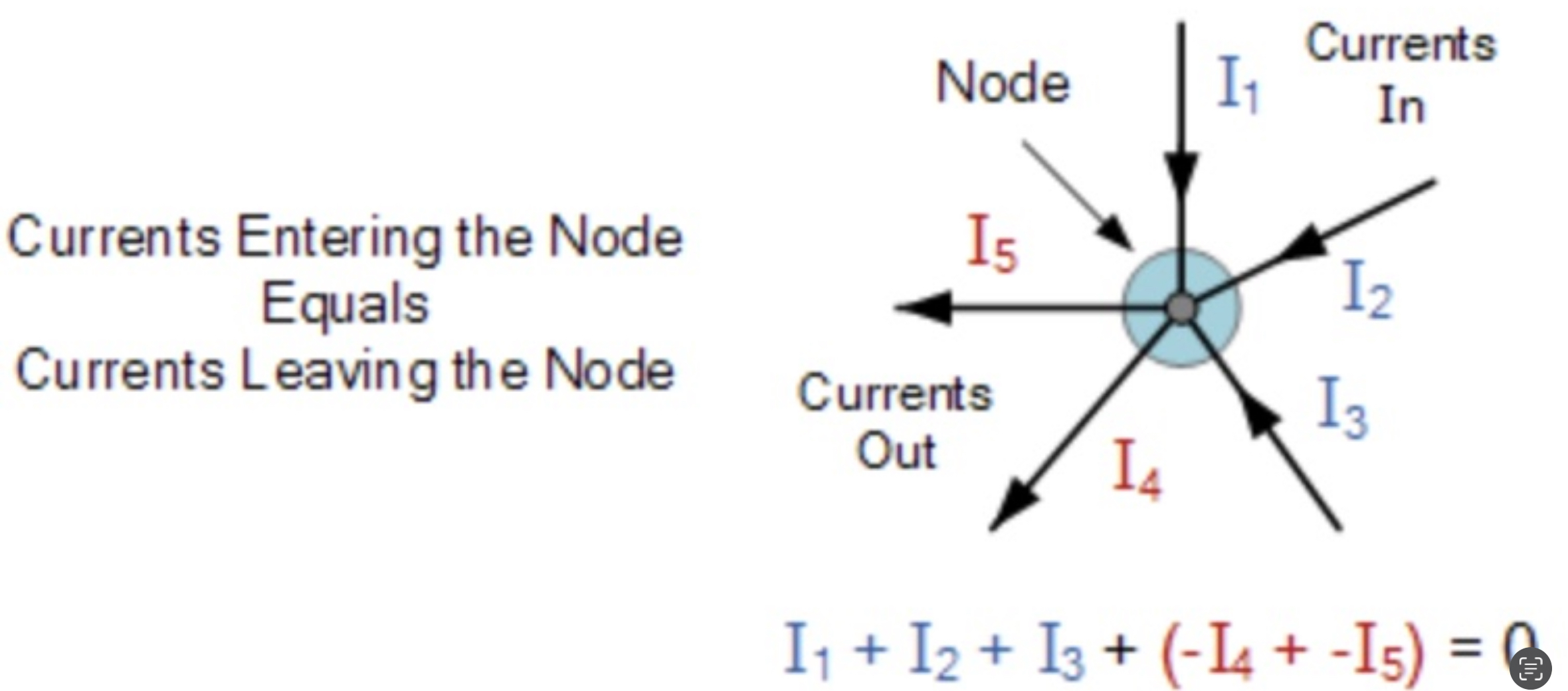
The term Node in an electrical circuit generally refers to a connection or junction of two or more current carrying paths or elements such as cables and components.
Electrostatics(정전기학) 에서의 기본법칙으로서 KCL (전자기학을 배우고 읽어보길...)
정전기학(정적 전기학)에서의 Ampere's Law는 다음과 같음.
$$ \nabla\times\text{H} =\text{J} $$
where
- $\text{H}$ : 정자기장.
- $\text{J}$ : 전류밀도.
위 식은 Stoke's theorem에 의해,
- 임의의 닫힌 경로 $C$를 따라 선적분한 $\oint_C\text{H}\cdot d\text{l}$은
- 폐경로 $C$를 경계로 가지는 surface를 통과하는 전체 전류의 양 $\unicode{x222f}_S\text{J}\cdot d\text{s}$과 같음을 의미.
또한, curl에 대한 divergence 는 항상 0이므로,
$$ \nabla \cdot \text {J}= \nabla \cdot \nabla \times \text {H}=0 $$
이 유도되며,
이는 node에서 유출되는 전류량과 유입되는 전류량은 같다는 아래의 식이 성립.
$$ \nabla \cdot \text {J}= \displaystyle { \lim_{\Delta v \to 0}} \frac {1}{ \Delta V} \oiint_S \text {J} \cdot d \text {s}=0 $$
위의 식이 성립되는 것은 정적 전기장에서 KCL 이 성립함을 의미.
하지만, Electrodynamics(전기장이 시간에 따라 변화하는 경우)에는 $\nabla \times \text {H} = \text {J} + \dfrac { \partial \text {D}}{ \partial t}$로 Ampere's law가 일반화되면서 실제 흐르는 전류가 아닌 displacement current density $\text{J}_d=\dfrac{\partial\text{D}}{\partial t}$ 가 추가되며, 위에 언급한 KCL에 보완이 필요함. (이를 통해 전파를 이용한 무선통신이 가능)
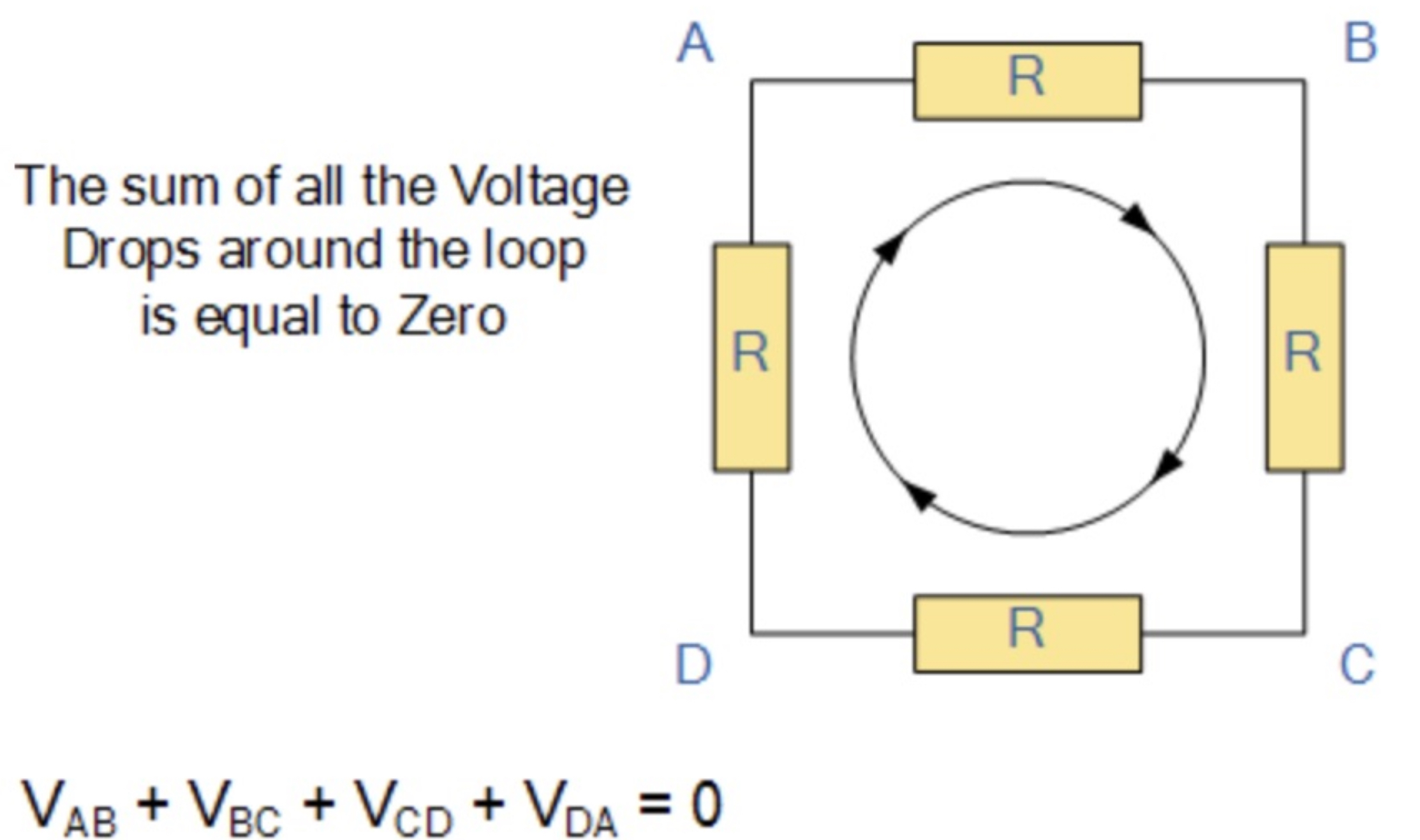
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL, 2법칙)
Kirchhoffs's Voltage Law or KVL, states that
“in any closed loop network, the total voltage around the loop is equal to the sum of all the voltage drops within the same loop”
which is also equal to zero.
In other words the algebraic sum of all voltages within the loop must be equal to zero.
This idea by Kirchhoff is known as the Conservation of Energy.
Electrostatics(정전기학) 에서의 기본법칙으로서 KVL (전자기학을 배우고 읽어볼 것)
$$\nabla \times \text {E}=0$$
- 위 식은 정전기장 $\text{E}$의 보존적(conservative)인 (회전이 없는) 성질을 나타냄.
- 스토크스의 정리(Stoke's theorem)에 의해 위의 식은 $\oint_C \text{E}\cdot d\text{l}=0$과 같은데, 이는 임의의 두 점 사이의 electric potential difference(전위차) 와 전압이 경로에 무관함을 의미함.
- 결국, 하나의 loop를 따라 측정한 voltage 의 합은 0이며, 이는 Kirchhoff's voltage law를 의미함.
Electrodynamics 에서는 Faraday's Law 에 의해
$$ \nabla \times \text{E} = -\dfrac{\partial\text{B}}{\partial t} $$
가 되며, 이는
$$ \oint_C\text{E}\cdot d\text{l}=-\unicode{x222F}_S\dfrac{\partial\text {B}}{\partial t}\cdot d\text{s} $$
로서 자기장의 음의 시간당 변화율을 면적분한 것이 closed loop를 따란 측정한 voltage의 합이 된다.
이는, 시간당 자기장의 변화율(고주파)이 클 경우, KVL이 성립하지 않음 을 의미함.
'정리필요. > 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 기업의 유형 (4) | 2024.09.30 |
|---|---|
| 대표적 전문직 소개 (3) | 2024.09.30 |
| 보고사항 및 기간 - 원자력법시행규칙 별표 [6] (0) | 2009.07.01 |
| 승인 - 방사선발생장치 또는 방사성동위원소가 내장된 기구 설계 (0) | 2009.06.27 |
| 신고 - 도난 분실 화재 (0) | 2009.06.26 |