Primitive Data Type이(Unboxed type)란?
C, C++, NumPy, PyTorch, TensorFlow 등에서 사용되는
numeric data type들은
보통 unboxed type 이라고도 불리는 primitive data type들이다.
- unboxed type에서는
- 할당된 메모리 bit들이 해당 numeric data type의 특정 값을 표현하는데 다 사용되고
- 해당 type이 고유의 meta data나 methods 등을 가지고 있지 않음.
- C프로그래밍을 배운 이들에게 이는 매우 당연하게 받아들여지는 개념이다.
- 이와 달리 boxed type이란,
- unboxed type처럼 값을 저장하는 메모리 bit들 외에도,
- 1) 가지고 있는 값에 대한 meta data 및
- 2) 값과 meta data를 처리를 할 수 있는 methods 등을 가지고 있어서
- 편리하지만, 추가적인 overhead를 가지고 있는 type을 의미한다.
- boxed type은 결국 class임: 실제 숫자값을 한 번 더 감싸는 abstraction이 이루어진 상태.
'Primal datatype' 또는 'Primitive datatype'은
프로그래밍 언어에서 가장 기본적이고 단순한 데이터 타입으로서
더 이상 작은 단위로 나눌 수 없고 기본적으로 제공되며 object가 아닌 단순 value를 저장함.
Python에서는
기본 numeric type들도 모조리 object이기 때문에 (사실 모든 것인 object의 하위 클래스 type임)
- reference count와 같은 meta data 및
- 자신의 type에 따른 methods를 제공한다.
이는 개발자에게 보다 편리한 기능을 제공하지만, 메모리나 성능의 측면 (특히 반복문)에서 희생이 불가피하다.
- primitive data type의 float (=32bit) type의 element가 백만개인 array에서는 정확히 사백만 bytes의 메모리만 있으면 되지만, Python에서의 float는 boxed type이며 이들을 element로 가지는 list도 object이기 때문에 그 이상의 메모리가 요구된다
(심지어 이들이 연속적으로 놓이다는 보장도 없음) - 대용량의 데이터를 다루는 경우에는 숫자 하나하나가 boxed type을 사용할 경우 효율이 극히 떨어지고 최적화가 매우 어렵다.
- boxed type을 사용할 경우, type checking이 요구되며,
- 이후 해당 type에 적절한 function 을 fetching하는 동작이
- 모든 연산에 부가적으로 들어가기 때문에 속도가 느림.
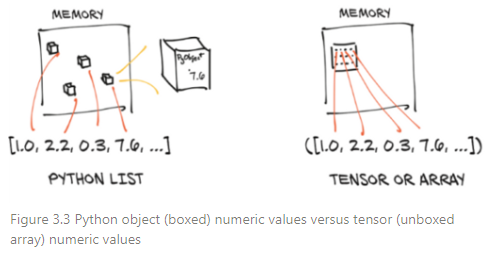
때문에 NumPy나 TensorFlow, PyTorch에서는 (최소한 내부의 storage layer상에서는)
unboxed type, primitive data type의 numeric type을 사용한다.
예를들어,
- PyTorch는 단일 element 접근 시 0D 텐서를 반환하여 사용자 관점에서는 boxed 타입처럼 보이지만,
- 텐서의 실제 저장은 raw memory buffer로 이루어지며 element는 unboxed primitive 타입으로 저장된다.
Tensor의 경우, storage layer에서는 C 에서의 array 형태(C-style contiguous array)의 데이터 구조로 저장됨.
array:
contiguous(접촉하는, 인접하는) memory blocks
containing homogeneous unboxed C numeric types
2023.06.22 - [.../Math] - [Math] Continuity (of Multivariable Function) and Contiguity
[Math] Continuity (of Multivariable Function) and Contiguity
Continuity (연속) 이란If $S\subseteq \mathbb{R}^n$, then a function $f:S\to \mathbb{R}$ is continuous at $\textbf{a} \in S$ if$$\begin{equation}\label{cont.def}\forall \varepsilon >0, \ \ \exists \delta>0 \mbox{ such that if } \mathbf x \in S \mbox{ an
dsaint31.tistory.com
C, C++
64bit Machine 및 64bit OS 기준 (LLP64)으로 정리함.
단, OS에 따라 차이가 있을 수 있으므로, sizeof 연산자를 통해 확인을 하는 것이 좋다.
정수형
(signed) char: 8bits, 1byteunsigned char: 8bits, 1byte(signed) short (int): 16bits, 2bytesunsigned short (int): 16bits, 2bytes(signed) long (int): 32bits, 4bytesunsigned long (int): 32bits, 4bytes(signed) int: 32bit, 4bytesunsigned int: 32bit, 4bytes
long long (int)의 경우 64bit임.
실수형
(signed) float: 32bits, 4bytes(unsigned) float: 32bits, 4bytes(signed) double: 64bits, 8bytes(unsigned) double: 64bits, 8bytes
기타 (64bit machine+64bit OS 기준)
Pointer: 64bits, 8bytes
C/C++ 의 경우, 데이터 모델이 위와 같은 LLP64 외에도 LP64도 있음(서버에선 LP64가 더 흔한 편.)
[C] LLP64 vs. LP64
LLP64와 LP64는 C/C++ 컴파일러가 데이터 타입의 크기를 정의하는 데이터 모델(data model) 임. LLP64와 LP64는 는 해당 모델이 어떤 타입들을 64비트로 처리하는지를 나타내는 이름을 가짐.long과 pointer가
ds31x.tistory.com
NumPy dtype 기준
bool_: Boolean (TrueorFalse) stored as abyteint_: Default integer type (same as C long; normally eitherint64orint32)intc: Identical to C int (normallyint32orint64)intp: Integer used for indexing (same as Cssize_t; normally eitherint32orint64)int8: Byte (-128 to 127)int16: Integer (-32768 to 32767)int32: Integer (-2147483648 to 2147483647)int64: Integer (-9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807) (numpy 기본)uint8: Unsigned integer (0 to 255)uint16: Unsigned integer (0 to 65535)uint32: Unsigned integer (0 to 4294967295)uint64: Unsigned integer (0 to 18446744073709551615)float_: Shorthand forfloat64. (numpy기본)float16: Half precision float: sign bit, 5 bits exponent, 10 bits mantissafloat32: Single precision float: sign bit, 8 bits exponent, 23 bits mantissafloat64: Double precision float: sign bit, 11 bits exponent, 52 bits mantissa (numpy 기본)complex_: Shorthand forcomplex128.complex64: Complex number, represented by two 32-bit floatscomplex128: Complex number, represented by two 64-bit floats
https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/arrays.scalars.html#
Scalars — NumPy v2.2 Manual
Scalars Python defines only one type of a particular data class (there is only one integer type, one floating-point type, etc.). This can be convenient in applications that don’t need to be concerned with all the ways data can be represented in a compute
numpy.org
Torch dtype 기준
PyTorch는 부동소수점에는 float32, 정수에는 int64를 기본으로 사용한다.
TensorFlow는 부동소수점에는 float32를 기본으로 사용하고, 정수에는 int32를 기본으로 사용한다.
torch.float32ortorch.float: 32-bit floating-point (Torch기본)torch.float64ortorch.double: 64-bit, double-precision floating-pointtorch.float16ortorch.half: 16-bit, half-precision floating-pointtorch.int8: signed 8-bit integerstorch.uint8: unsigned 8-bit integerstorch.int16ortorch.short: signed 16-bit integerstorch.uint16: unsigned 16-bit integerstorch.int32ortorch.int: signed 32-bit integerstorch.uint32: unsigned 32-bit integerstorch.int64ortorch.long: signed 64-bit integers (Torch기본)torch.bool: Booleantorch.complex64: complex numbers (32-bit real + 32-bit imaginary)torch.complex128or torch.cdouble: complex numbers (64-bit real + 64-bit imaginary)torch.complex32ortorch.chalf: complex numbers (16-bit real + 16-bit imaginary)
TensorFlow도 float32를 기본으로 사용하지만,
Torch와 달리 TensorFlow는 int의 경우엔 int32가 기본임.
PyTorch에서 uint16과 uint32는 비교적 덜 일반적으로 사용되며,
주로 특수한 케이스(예: 특정 이미지 처리나 메모리 최적화)에서 사용.
대부분의 PyTorch 연산은 기본적으로 float32(부동소수점)나 int64(정수)를 사용하도록 설계.
PyTorch는 complex32도 지원함: TensorFlow는 미지원
더불어 위의 표에선 나타내지 않았으나, PyTorch도 bfloat16을 지원하고 있음.
[PyTorch] dtype 단축메서드로 바꾸기
아래의 URL에서 간단히 다룬 단축 method들을 이용한 방식 (to나 type이 아닌)을 설명하는 문서임.2024.03.15 - [Python] - [DL] Tensor: dtype 변경(casting) 및 shape 변경. [DL] Tensor: dtype 변경(casting) 및 shape 변경.Ten
ds31x.tistory.com
TensorFlow dtype 기준
tf.float32ortf.float: 32-bit floating-point (TensorFlow기본)tf.float64ortf.double: 64-bit, double-precision floating-pointtf.float16ortf.half: 16-bit, half-precision floating-pointtf.bfloat16: 16-bit brain floating-point (TPU/CPU 최적화용)tf.int8: signed 8-bit integerstf.uint8: unsigned 8-bit integerstf.int16: signed 16-bit integerstf.uint16: unsigned 16-bit integerstf.int32ortf.int: signed 32-bit integers (TensorFlow 기본)tf.int64ortf.long: signed 64-bit integerstf.uint32: unsigned 32-bit integerstf.uint64: unsigned 64-bit integerstf.bool: Booleantf.complex64: complex numbers (32-bit real + 32-bit imaginary)tf.complex128: complex numbers (64-bit real + 64-bit imaginary)tf.string: variable-length string
주요 차이점:
- TensorFlow는
bfloat16타입을 추가로 지원 (Google의 TPU를 위해 설계됨) - TensorFlow는
string타입을 추가로 지원. - TensorFlow의 기본 정수형은
int32인 반면, PyTorch는int64가 기본.
참고
size_t:size type임.- 즉, size를 나타내기 위한 type으로 보통
unsigned int임. sizeof의 반환값의 타입.
ssize_t:signed size type임.- I/O 함수의 반환값으로 처리된 size를 나타내거나
-1등으로 연산의 실패 등을 표시함. - 보통
signed int임 .
C/C++ 의 경우 이식성을 위해서 고정폭의 데이터 타입들도 지원함.
int32_t, int64_t 등이 대표적인 명확한 고정폭 타입.
'Programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [NumPy] searchsorted (0) | 2023.03.29 |
|---|---|
| [Basic] Literal (0) | 2023.02.20 |
| [PyQt] Event and Event Handling 작동방식 (0) | 2023.01.26 |
| [Programming] Library vs. Framework (0) | 2023.01.18 |
| [PyQt6] Install PyQt6 on Windows (2) | 2023.01.03 |