Moment (모멘트)
어떤 물리적인 effect(e.g.회전운동)등을 정량화하는 물리량의 일종으로 그 크기가
- 하나의 물리량(e.g. mass) 뿐 아니라
- 해당 물리량의 분포(or 위치) 까지 고려하여
정해지는 경우 moment라고 부름.
Momentum (운동량)과의 구분
momentum (운동량)과 헷갈리면 안됨.
momentum은 물리에서 물체의 질량(mass)과 속도(velocity)의 곱으로,
물체가 가진 운동의 양을 의미함. 즉, 물체가 얼마나 빠르고 무겁게 움직이는지를 나타내는 물리량임.
이름의 유래는 다음을 참고할 것.
“Moment”는 라틴어 “momentum”에서 유래하였으나,
현대 물리와 공학에서 “Moment”는 힘이나 질량이 특정 축을 기준으로 어떻게 분포되어 있는지를 설명하는 데 사용됨.
물리학에서 **힘(force)**이 특정한 축을 기준으로 물체에 미치는 영향을 설명할 때 사용되며, 이때 힘이 작용하는 위치에 따라 물체의 움직임이나 변화가 달라짐. 그래서 “moment”는 중요한 순간 또는 영향을 나타내는 의미로 발전하였음.
시간이 지나면서 이 개념은 확장되어, 확률(probability), 물리(physics), 그리고 영상처리(image processing)와 같은 다양한 분야에서 값들이 중심에서 얼마나 떨어져 있는지를 설명하는 중요한 도구로 자리 잡음.
이를 통해 “moment”는 값의 분포(distribution of values)와 그로 인한 특성을 분석하는 개념으로 발전하게 되었음.
설명
“Moment”는 다양한 분야에서 값의 분포를 설명하는 데 사용되며,
공통적으로 값들이 어떻게 분포되어 있고 그 값들이 중심에서 얼마나 떨어져 있는지를 고려함.
가장 유명한 것이 torque로서 torque 는 1차 moment of force 임.
즉, torque ($\vec{\tau}$)의 크기에는
- force라는 물리량($\vec{F}$)과 함께,
- 해당 force의 작용점이 회전중심으로 떨어진 거리($\vec{r}$)가 함께 고려됨.
$$\vec{\tau}=\vec{r} \times \vec{F}$$
여기서 물리량은 vector가 될 수 있기 때문에 moment를 구하기 위해 사용되는 곱(multiplication)은
- inner-product,
- cross-product 등이 될 수 있음.
또한 일반적으로 영향을 주는 물리량의 위치에 해당하는 정보는 어떤 reference point로부터의 거리 등을 사용함
또한 해당 위치에 해당하는 정보는 몇 제곱이 이루어져 물리량과 곱해주는 형태를 취함.
- 물리량 위치에 해당하는 정보를 그대로 곱하면 1차 moment,
- 제곱하여 곱하면 2차 moment라고 부름 (즉, 차수를 결정)
$$n\text{-th moment} =\text{(위치 or 분포 물리량)}^n \times \text{(물리량)}$$
이를 수식으로 표현하면 다음과 같음.
$$\mu_n=r^n \times Q$$
where
- $\mu_n$ : $n$ th moment
- $Q$ : 기본이 되는 physical qunatity
- $r$ : distance from reference point
- $\times$ : product. scalar product일수도 있고 vector product일수도 있음.
위치나 분포를 나타내는 물리량은 일반적으로 어떤 reference point로부터의 거리로 기재되며, 기본으로 사용하는 물리량이 공간에 퍼져있는 경우 각각의 포인트에 대해 moment를 구한 후 이를 적분하는 형태를 취함. 즉 다음과 같음.
$$\mu_n = \int r^n \times \rho(r) dr$$
where
- $\rho(r)$ : $Q$에 해당하는 물리량의 $r$위치에서의 밀도임.
전형적인 예가 회전운동에 대한 관성(rotational inertia)을 의미하는 2nd moment of mass임.
이 경우 회전중심이 reference point가 된다. 다음은 회전축과 mass의 분포에 따른 rotational inertia을 보인 그림임.
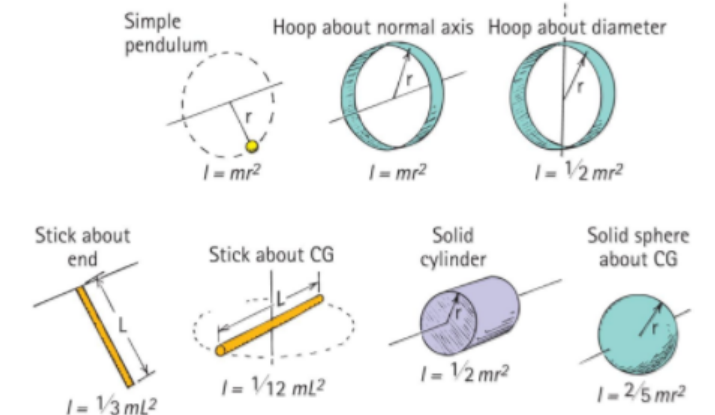
회전축과 mass의 분포에 따라 식이 다르지만, $mL^2$ 또는 $mr^2$의 형태를 취하고 있다.
즉, mass의 2차 모멘트임을 확인할 수 있다.
비교
다양한 분야에서의 Moment에 대한 비교를 표로 정리하면 다음과 같음.
| definition | 1st moment | 2nd moment | application | |
| Physics | 힘이나 질량이 공간에서 분포된 정도와 회전 운동을 설명 | 물체의 힘이나 질량 중심 |
물체의 회전 저항 (관성 모멘트) |
데이터 분석, 분포의 형태 설명 |
| Probability | 데이터의 퍼짐과 중심을 설명 | 데이터의 중심 (평균) |
데이터의 퍼짐 (분산) |
회전 운동 분석, 기계 설계, 구조물 분석 |
| Image Processing | 이미지의 픽셀 값들이 공간에서 어떻게 퍼져 있는지 설명하는 도구 | 이미지의 중심 (centroid) |
이미지의 변형에 따른 형태 분석 |
물체 인식, 패턴 분석, 이미지 회전 및 이동 인식 |
다음 글을 읽어보면 moment의 개념이 좀 더 명확해질 듯...
Moment
-
In physics, a moment is a turning effect (회전관련) of a force.
-
It is an expression involving the product of a distance and a physical quantity, and in this way it accounts for how the physical quantity is located or arranged.
-
Moments are usually defined with respect to a fixed reference point; they deal with physical quantities as measured at some distance from that reference point.
-
For example, the moment of force acting on an object, often called torque, is the product of the force and the distance from a reference point.
-
In principle, any physical quantity can be multiplied by distance to produce a moment; commonly used quantities include forces, masses, and electric charge distributions.
Moment 용어 관련 자료들
영상처리에서의 moment :https://dsaint31.me/mkdocs_site/DIP/cv2/ch02/dip_contour_features/#moment
BME228
Contour Features Moment Image moments은 물체의 중심, 물체의 면적 등을 계산하는데 이용되는 quantity(양)임. pixel intensity(←물리에서 force, mass등)의 정량적 크기 와 함께 분포 (어떤 기준에 대한) 를 고려한
dsaint31.me
확률 및 통계 에서의 moment : 2022.03.31 - [.../Math] - [Statistics] Moment (Probability Moment)
[Statistics] Moment (Probability Moment)
1. Moment (Probability Moment) : Statistics 💡 statistics에서 moment는 probability distribution에서 계산되어진 특징값 확률 분포를 이용하여 구해지는 random variable의 대표값(or 통계량)을 일반화(generalization)시킨
dsaint31.tistory.com
역학(회전)에서의 moment :2022.05.09 - [.../Physics] - [Physics] Moment of inertia (관성모멘트)
[Physics] Moment of inertia (관성모멘트)
회전운동을 유지하려고 하는 회전 관성의 정도를 정량화한 scalar quantity. rotational inertia(회전관성)이라고 불림. inertia의 정도는 mass에 의해 결정되므로 moment of mass라고 할 수 있음. (실제로 2차 모
dsaint31.tistory.com
2022.05.09 - [.../Physics] - [Physics] Moment of Force (or Torque)
[Physics] Moment of Force (or Torque)
물체의 회전 또는 회전운동의 원인 더보기 Torque : The tendency of a force to cause rotation Torque depends upon three factors: Magnitude of the force The direction in which it acts The point at which it is applied on the object 물체를
dsaint31.tistory.com
'... > Physics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Physics] Moment of inertia (관성모멘트) (0) | 2022.05.09 |
|---|---|
| Lever : 인체지레 (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| [Physics] Circular Motion (원운동) (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| [Physics] Moment of Force (or Torque) (0) | 2022.05.09 |
| [Physics] A periodic representation of wave : sin and cos (0) | 2022.04.19 |