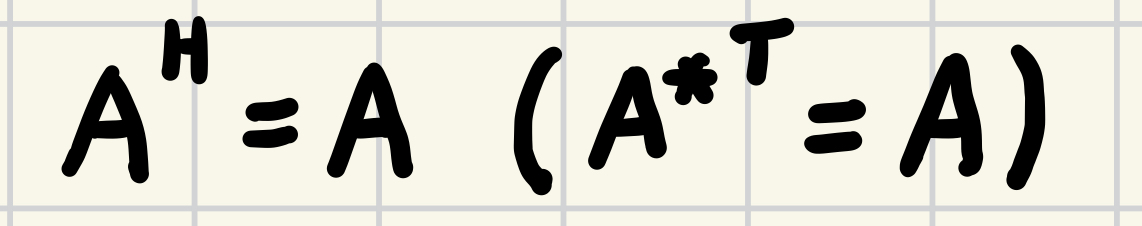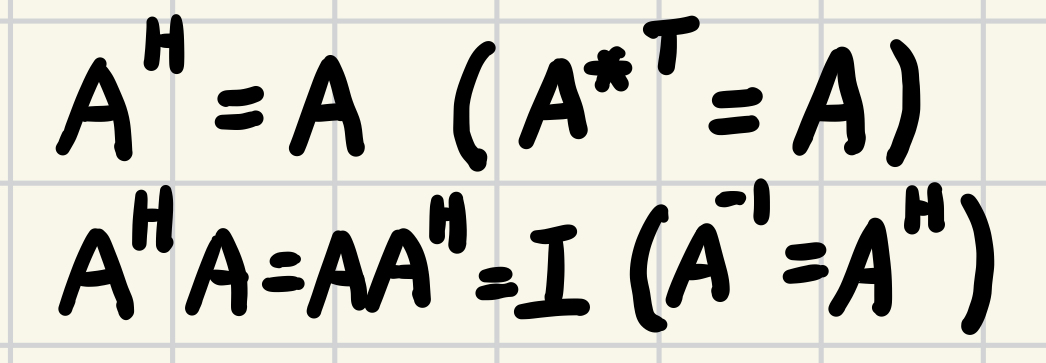
0. Definition of Hermitian Matrix
모든 entity들에 complex conjugate를 취하고 Transpose를 할 경우, 자기자신이 나오는 matrix.
$$A={A^*}^\top(=A^H)$$
- complex conjugate를 취하고 tanspose하는 연산을 Herimitian adjoint (에르미트 수반) 또는 줄여서 adjoint라고 부름: 다른 이름으로 켤레전치(conjugate transpose)라고도 불림. $A^\dagger$로 표기하기도 함.
- 역행렬을 구할 때 cofactor들로 구성된 행렬의 transpose도 adjoint matrix 또는 줄여서 adjoint라고 불렸었는데
- 이를 Hermitian adjoint와 구분하기 위해 최근엔 classic adjoint 또는 adjugate 라고 부름.
- Normal Matrix의 일종.
실수에서의 symmetric matrix를
복소수로 확장한 것이 Hermitian matrix임.
Hermitian matrix중 특별한 것이
Symmetric matrix임(실수로 한정시킴)
Hermitian Symmetry가 성립하는 Matrix라고 볼 수 있음.
https://bme808.blogspot.com/2022/11/math-hermitian-symmetry.html
Math : Hermitian Symmetry
Hermitian symmetry는 complex function 또는 complex matrix에서의 대칭성 중 하나임. Hermitian Symmetry for Complex Function real number에서의 symm...
bme808.blogspot.com
함수에서도 Hermitian Symmetry가 가능한데,
- compelx conjugate를 가하는 건 같고
- transpose는 독립변수에 reflection 연산을 취하는 것임.
$$f(-x)=f^*(x)\quad \text{or}\quad f(x)=f^*(-x)$$
1. Hermitian Matrix의 성질
$A$가 Hermitian matrix인 경우 다음이 성립함.
1-1. $\textbf{x}^HA\textbf{x}$는 항상 Real Number(실수)임.
$\textbf{x}^H$는 $\textbf{x}$에 대해 complex conjugate를 취하고 transpose를 시키는 conjugate tanspose를 의미함. vector외에 matrix에도 취할 수 있음.
우선, $\textbf{x}^HA\textbf{x}(={\textbf{x}^*}^\top A\textbf{x})$는 scalar (or $1\times 1$ matrix)임 (quadratic form은 scalar-valued function).
- scalar의 경우, transpose를 취해도 같은 값임. (scalar를 $1\times 1 matrix$로 생각)
이에 따라 다음이 성립 [$z^*$는 $z$에 대한 complex conjugate를 의미함].
$$\left({\textbf{x}^*}^\top A\textbf{x}\right)^*=\left[\left({\textbf{x}^*}^\top A\textbf{x}\right)^*\right]^\top=\left[\textbf{x}^\top A^*\textbf{x}^*\right]^\top ={\textbf{x}^*}^\top{A^*}^\top \textbf{x}$$
위 식에서 $A$가 Hermitian matrix ($A={A^*}^\top=A^H$)이므로, 다음이 성립함
$$\left({\textbf{x}^*}^\top A\textbf{x}\right)^*={\textbf{x}^*}^\top {A^*}^\top \textbf{x}={\textbf{x}^*}^\top A\textbf{x}$$
앞서 말한대로, scalar이므로 transpose해도 같아야 하며, 자신과 자신의 complex conjugate가 같으므로 ${\textbf{x}^*}^ \top A\textbf{x} (= \textbf{x}^HA\textbf{x})$는 real number이어야만 한다.
1-2. Hermitian Matrix $A$ 의 Eigenvalue는 모두 실수임.
$\lambda$를 $A$의 Eigenvalue라고 하고, $\textbf{x}$를 $\lambda$에 대응하는 eigen vector라고 하면, 다음이 성립함.
$$\textbf{x}^HA\textbf{x}=\textbf{x}^H\lambda\textbf{x}=\lambda \textbf{x}^H\textbf{x}=\lambda \|\textbf{x}\|^2$$
$\textbf{x}^HA\textbf{x}$는 real number이며, $\|\textbf{x}\|^2$도 0이 아니므로(eigen vector는 정의에서부터 zero vector가 아니기 때문에 norm이도 0이 아닌 positive real number임), $\lambda$도 real number여야만 함.
Normal Matrix는 Eigenvalue가
complex number일 수 있는 것과 차이점.
1-3. Hermitian Matrix $A$ 의 distinct한 Eigenvalue들에 대응하는 eigen vector들은 서로 orthogonal함.
$\textbf{v}_1$과 $\textbf{v}_2$가 $A$의 eigen vector이고, 이에 대응하는 Eigenvalue가 $\lambda_1,\lambda_2$라고 하면 다음이 성립함.
$$\begin{aligned} \lambda_1 \textbf{v}_1 \cdot \textbf{v}_2 &= (\lambda_1 \textbf{v}_1)^\top \textbf{v}_2 = (A\textbf{v}_1)^\top \textbf{v}_2 & \text{ Since } \textbf{v}_1 \text{ is an eigenvector} \\ &= (\textbf{v}_1^\top A^\top)\textbf{v}_2 = \textbf{v}_1^\top (A \textbf{v}_2) & \text{ Since } A^\top = A \\ &= \textbf{v}_1^\top (\lambda_2 \textbf{v}_2) & \text{ Since } \textbf{v}_2 \text{ is an eigenvector} \\ &= \lambda_2 \textbf{v}_1^\top \textbf{v}_2 = \lambda_2 \textbf{v}_1 \cdot \textbf{v}_2 \end{aligned}$$
$(\lambda_1 - \lambda_2) \textbf{v}_1 \cdot \textbf{v}_2 = 0$이 성립하는데, $\lambda_1 \ne \lambda_2$이므로 결국, 다음이 성립.
$$\textbf{v}_1 \cdot \textbf{v}_2 = 0. $$
2. Unitary Matrix와의 관계
만약 multiplicity인 Eigenvalue에 해당하는 Eigenspace에서 해당 multiplicity와 같은 수의 Orthogonal Eigenvector를 가질 경우, Unitary matrix $U$가 됨.
$$U^H U= U U^H = I \\ U^H = U^{-1}$$
Unitary Matrix는
실수에서의 Orthogonal Matrix를
복소수로 확장한 것임.
참고로, Fourier Transform에 해당하는 matrix $F$가 바로 Unitary Matrix임.
$$F_{m,n} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{N}}e^{-j \frac{2\pi}{N}mn}$$
where
- $N$: matrix의 크기 (square matrix로 행과 열이 모두 $N$개임)
- $m,n$: 행과 열의 index.
같이 보면 좋은 자료들
2022.11.17 - [.../Math] - [LA] Normal Matrix (정규행렬)
[LA] Normal Matrix (정규행렬)
Normal Matrix란?Matrix $A \in M_n (C)$에 대해 (◀ Matrix가 Complex Number를 가질 수 있으며, $n\times n$ Square Matrix임), 다음을 만족하면 $A$를 Normal Matrix (정규행렬)이라고 부름.$$A\bar{A}^\top(=AA^*)=\bar{A}^\top A(=AA^*)$
dsaint31.tistory.com
'... > Math' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Math] ill-posed, well-posed, ill-conditioned, well-conditioned matrix (or problem) (2) | 2022.12.02 |
|---|---|
| [LA] 예제: Eigenvalue, Eigenvector 구하기 (0) | 2022.12.01 |
| [LA] Orthogonal Matrix (직교행렬) and Orthonormal Vector (0) | 2022.11.17 |
| [LA] Normal Matrix (정규행렬) (0) | 2022.11.17 |
| [Math] Multi-variable vs. Multi-variate and Multiple Regression (0) | 2022.11.17 |